The journey of humanoid robotics has captivated imaginations for decades, blending science fiction with cutting-edge technology. From It Is A Human Like Robot That Was Created By Honda In The Year 2000 to the dynamic capabilities of Boston Dynamics’ Atlas, the evolution of human-like robots reflects remarkable advancements in AI, engineering, and human-machine interaction. This article traces key milestones, explores technical challenges and breakthroughs, and addresses the burning question: Is It Possible To Make A Robot That Looks Like A Human? Let’s dive into the timeline and uncover how far we’ve come in creating robots that mimic human form and function.
The Dawn of Humanoid Robotics: Honda’s ASIMO
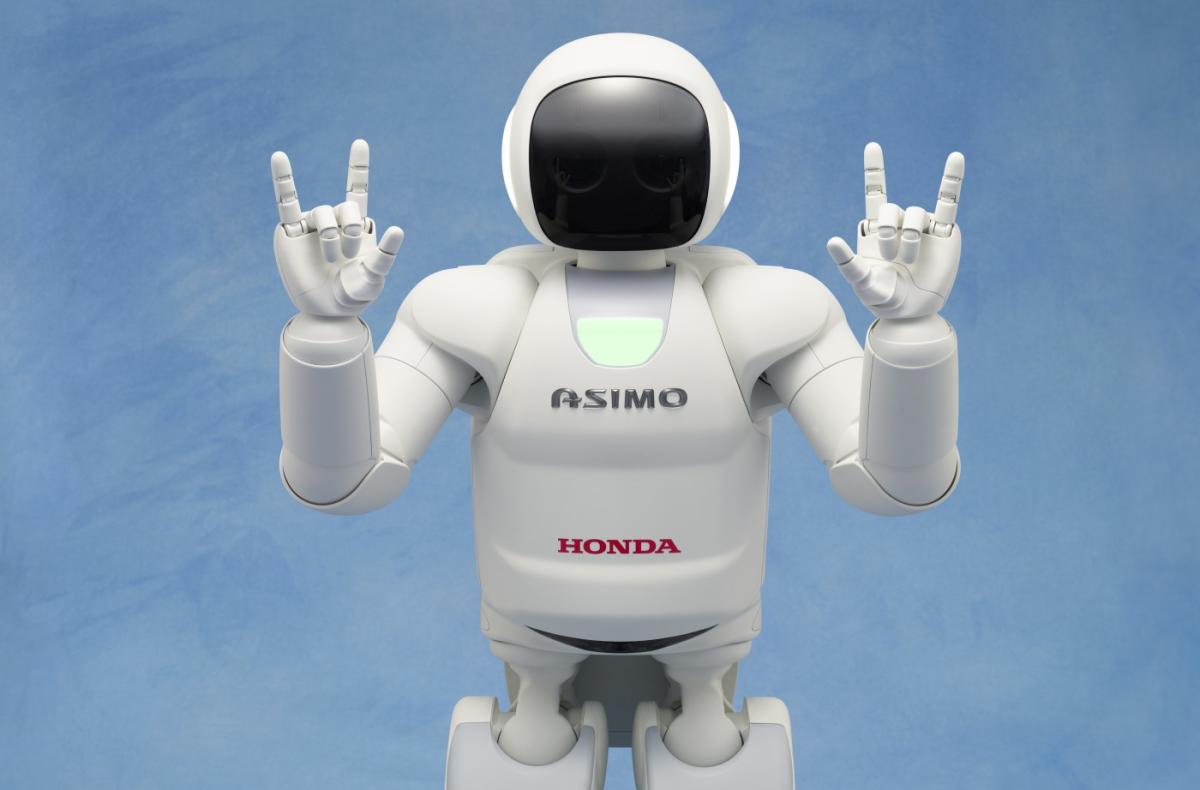
In 2000, Honda unveiled ASIMO, a groundbreaking humanoid robot that marked a significant leap in robotics. Standing at 4 feet 3 inches and weighing 119 pounds, ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility) was designed to assist humans in daily tasks. Its development began in 1986 with Honda’s E-series, focusing on bipedal locomotion, followed by the P-series, which introduced human-like proportions. By 2000, ASIMO could walk, climb stairs, and perform simple tasks like opening a bottle and pouring water, showcasing early AI-driven autonomy and sensor integration.
ASIMO’s ability to navigate human environments, recognize faces, and respond to voice commands made it a global sensation. Its lightweight magnesium alloy frame and 51.8V lithium-ion battery allowed for an hour of operation, a feat for its time. Honda’s focus on safety and human interaction set a high standard, influencing future humanoid designs. To learn more about AI’s role in robotics, check out our comprehensive resources Explore AI Innovations.
Evolution Through the Years: Key Milestones
1986–1997: Honda’s Early Prototypes
Honda’s journey began with the E0 prototype in 1986, a basic bipedal walker. The E-series (1986–1993) and P-series (1993–1997) refined walking mechanics, with P3 achieving a compact 130 kg design. These laid the groundwork for ASIMO’s debut.
2000: ASIMO’s Grand Unveiling
It Is A Human Like Robot That Was Created By Honda In The Year 2000. ASIMO introduced dynamic walking, stair-climbing, and basic human interaction, earning a spot in the Carnegie Mellon Robot Hall of Fame in 2004.
2005–2011: ASIMO’s Upgrades
By 2005, ASIMO could run at 6 km/h and perform tasks like serving drinks. The 2011 model boasted enhanced autonomy, recognizing multiple voices and navigating crowded spaces, pushing the boundaries of human-robot coexistence.
2013–2024: Boston Dynamics’ Atlas Emerges
Atlas, developed by Boston Dynamics, shifted the focus to robust physical capabilities. Initially funded by DARPA for disaster response, Atlas could perform backflips and parkour by 2018. Its electric version, unveiled in 2024, emphasizes real-world applications.
Technical Challenges in Building Human-Like Robots
Creating a robot that mirrors human movement and interaction is no small feat. Key challenges include:
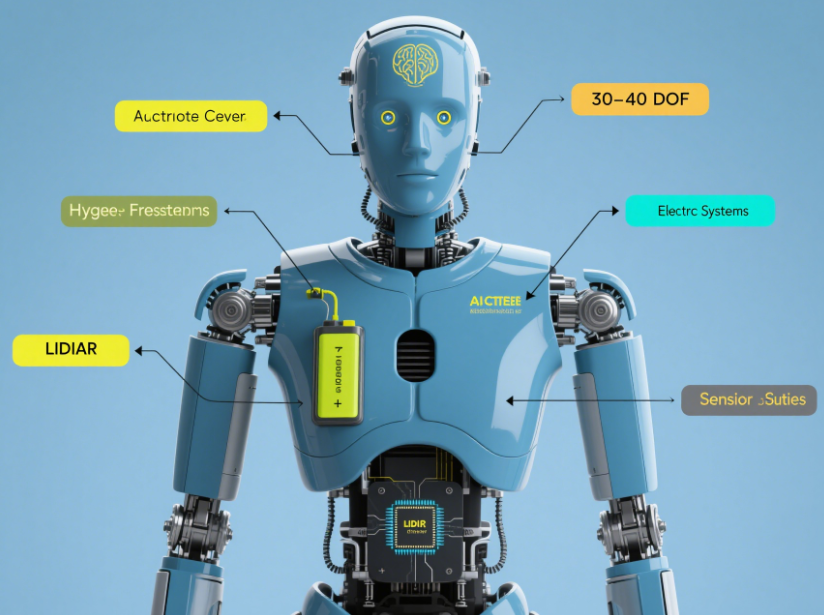
Balance and Locomotion: Maintaining stability during dynamic movements like running or navigating uneven terrain requires advanced sensors (e.g., gyroscopes, LIDAR) and real-time algorithms. ASIMO used Zero Moment Point (ZMP) control, while Atlas leverages hydraulic and electric systems for agility.
Dexterity: Human-like hands, as seen in ASIMO’s multi-fingered design, demand precise force control. Atlas’s hands are built for heavy-duty tasks, but achieving human-level dexterity remains complex.
Autonomy and AI: Early robots like ASIMO relied on preprogrammed actions, but modern AI enables Atlas to make real-time decisions. Integrating machine learning for natural interactions is still a work in progress.
Energy Efficiency: ASIMO’s one-hour battery life highlighted the challenge of power density. Atlas’s electric design improves runtime, but energy-efficient humanoids remain a goal.
Safety: Ensuring robots don’t harm humans during falls or collisions is critical. Honda prioritized safety in ASIMO, while Atlas’s robust design poses new safety considerations.
Breakthroughs That Shaped the Future
Several innovations have propelled humanoid robotics forward:
Sensor Integration: ASIMO’s cameras, ultrasonic, and tactile sensors enabled obstacle detection and interaction. Atlas’s LIDAR and stereo vision enhance environmental awareness.
AI Advancements: Machine learning has transformed robots from scripted performers to adaptive agents. Atlas’s ability to learn from its environment builds on ASIMO’s foundational AI support.
Material and Design Improvements: Lightweight materials like ASIMO’s magnesium alloy and Atlas’s advanced composites reduce weight while maintaining strength.
Commercial Viability: While ASIMO was a research platform, Atlas’s electric version aims for practical applications, from industrial tasks to disaster response.
Curious about how these breakthroughs impact AI development? Discover more AI Technology Insights.
Is It Possible To Make A Robot That Looks Like A Human?
Today, creating a robot that looks and acts like a human is closer to reality than ever, but significant hurdles remain. Advances in materials allow for lifelike appearances, as seen in robots like Hanson Robotics’ Sophia, which uses expressive facial designs. However, mimicking human behavior—natural speech, emotional intelligence, and fluid movement—requires sophisticated AI and vast computational power. Atlas demonstrates physical prowess, but its industrial design prioritizes function over human-like aesthetics.
Technical limitations, such as battery life and processing speed, still hinder fully autonomous human-like robots. Social acceptance and ethical concerns also play a role, as society grapples with robots in daily life. While Is It Possible To Make A Robot That Looks Like A Human? Yes, it’s feasible for specific applications, but a universally human-like robot for homes or workplaces is likely a decade away, requiring further AI and energy breakthroughs.
FAQs
What made Honda’s ASIMO unique?
ASIMO was the first humanoid robot to achieve dynamic bipedal walking, climb stairs, and perform tasks like pouring drinks. Its focus on human-robot interaction and safety set it apart.
How does Atlas compare to ASIMO?
ASIMO emphasized human-like interaction and mobility in controlled environments, while Atlas prioritizes physical robustness and autonomy for challenging tasks like disaster response.
Why did Honda retire ASIMO?
Honda halted ASIMO’s development in 2018 to focus on practical applications, such as disaster response and elder care, using ASIMO’s technologies in more specialized robots.
[](https://www.theverge.com/2018/6/28/17514134/honda-asimo-humanoid-robot-retire)Can we expect human-like robots in homes soon?
While advancements are rapid, fully human-like robots in homes face challenges like energy efficiency and cost. Widespread adoption may occur in the 2030s.
Conclusion
From It Is A Human Like Robot That Was Created By Honda In The Year 2000 to the agile Atlas, the evolution of humanoid robots showcases humanity’s drive to blend technology with human-like capabilities. While ASIMO pioneered human-robot interaction, Atlas pushes the boundaries of physical performance. The question, Is It Possible To Make A Robot That Looks Like A Human, highlights ongoing challenges and exciting possibilities. As AI and robotics advance, the dream of human-like robots in daily life grows closer, promising a future where they assist and inspire.