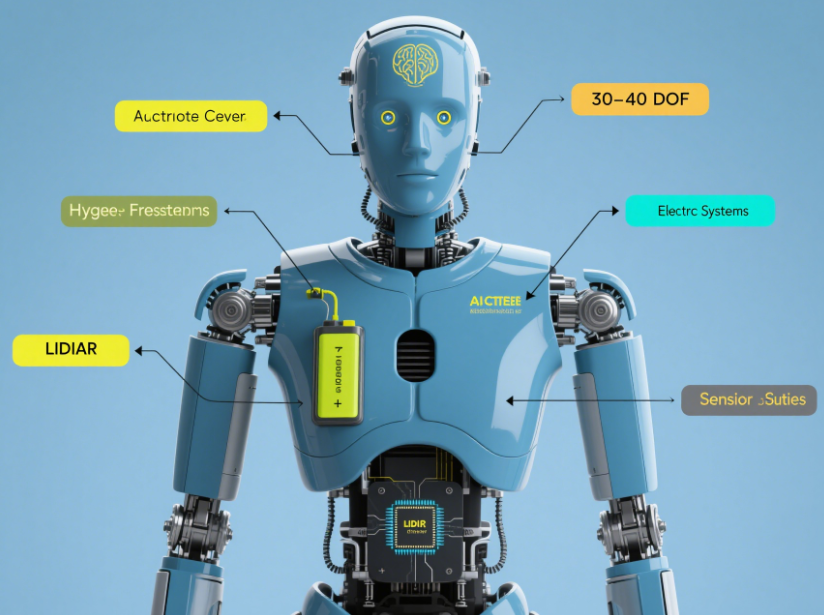
Imagine a machine that walks like you, gestures like you, and interacts with human-like fluidity. This isn't science fiction anymore - it's the reality of In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android. Unlike the standardized robots bolted to factory floors, androids represent robotics' most ambitious endeavor: creating machines in our own image. The global race to perfect these humanoid marvels is accelerating, with China's market projected to explode from 2.76 billion yuan in 2024 to 300 billion yuan by 2035, signaling a technological shift that will redefine industries from healthcare to hospitality .
In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android: Definition and Origins
When we ask In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android, we're specifically discussing robots designed to mimic the human form and behavior with high fidelity. The term originates from the Greek "andr-" (meaning man) and "-oid" (meaning resembling), essentially translating to "human-like" . This concept dates back to 1886 when French author Auguste Villiers de l'Isle-Adam first used "Android" in his sci-fi novel "L'ève future" to describe human-appearing machines .
What fundamentally distinguishes androids from other robots is their intentional biomimicry. While industrial robots prioritize function over form, androids deliberately replicate human kinematics, sensory systems, and interaction patterns. This enables them to operate in human-engineered environments without infrastructure redesign - climbing stairs meant for human legs, manipulating tools designed for human hands, and navigating spaces scaled to human dimensions .
In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android Versus Conventional Robots
Understanding In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android requires recognizing how they diverge from traditional robotics:
| Feature | Android Robots | Traditional Robots |
|---|---|---|
| Form Factor | Human-like body plan (bipedal stance, opposable thumbs, facial features) | Functional designs (articulated arms, wheels/tracks, no human resemblance) |
| Mobility | Bipedal or human-like locomotion (walking, climbing stairs) | Stationary or wheel/track-based movement |
| Interaction Mode | Natural language, facial expressions, gesture recognition | Programmed interfaces, control panels, limited voice commands |
| Operating Environment | Human spaces (homes, hospitals, public facilities) | Controlled environments (factories, warehouses, laboratories) |
| Primary Function | Social interaction, caregiving, adaptable service tasks | Repetitive manufacturing, precision assembly, heavy lifting |
A critical linguistic distinction: "Android" specifically references male-presenting humanoid robots, while "Gynoid" describes female-presenting versions. This gender differentiation, though often overlooked commercially, remains embedded in the terminology's technical roots .
The In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android Revolution: Global Progress
Technological Milestones
Recent breakthroughs have transformed androids from laboratory curiosities into functional machines. China's 2024 "Tiangong" android made history as the first full-sized electrically-driven humanoid capable of dynamic running , while the United States' Figure AI deployed second-generation androids in BMW factories where they handle complex tasks through AI-driven environmental learning .
Market Expansion
The android sector is experiencing explosive investment, with 56 of the 69 global humanoid robot funding rounds in 2024 occurring in China alone . The International Robotics Federation reports 410,000 consumer service robots installed globally in 2023, a sector dominated by increasingly human-like models .
Industrial Integration
Real-world deployment is accelerating beyond demonstrations. The Walker S1 android at Chinese automaker BYD performs vehicle inspections in seconds, while others coordinate with autonomous forklifts and logistics robots, creating fully automated workflows . This represents the tangible implementation of In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android in commercial environments.
Where In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android Makes Impact: Application Sectors
Androids excel where tasks require human-like physical interaction or social engagement. Their anthropomorphic design enables natural operation in human-centric environments without costly infrastructure modifications - a revolutionary advantage over conventional robotics.
Healthcare and Personal Assistance
Androids are entering caregiving roles, supporting elderly individuals with mobility assistance, medication reminders, and companionship. Their ability to interpret natural speech and recognize facial expressions enables emotionally intelligent interactions impossible with earlier robots .
Specialized Industrial Services
In manufacturing, androids like Walker S handle quality inspections and equipment monitoring in environments where traditional automation struggles. Their human-like dexterity allows them to operate machinery designed for human workers .
Hospitality and Customer Service
From hotel concierges to restaurant hosts, androids provide 24/7 service with consistent quality. China's 2023 commercial service robot market grew 17.6% annually, with delivery models leading adoption .
Emergency Response
Android platforms navigate disaster zones too hazardous for humans, performing search and rescue operations with human-equivalent mobility. Their bipedal design accesses areas inaccessible to wheeled or tracked robots .
Tomorrow's In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android: Emerging Capabilities
The next evolutionary phase for androids centers on cognitive sophistication. With embodied AI integration, these machines are developing contextual awareness and decision-making autonomy. China's "CASBOT 01" demonstrates unprecedented adaptability, traversing everything from the Great Wall's uneven steps to Gobi Desert terrain .
Three transformative developments are accelerating android capabilities:
Generative AI Interfaces
Natural language programming allows non-technical personnel to instruct androids using verbal commands rather than code. This democratizes robot operation across workforce skill levels .
Predictive Maintenance Intelligence
Machine learning algorithms analyze performance data to anticipate mechanical failures before they occur. Given that automotive industry robot downtime costs approximately $1.3 million hourly, this represents massive value preservation .
Multi-Agent Collaboration Systems
Advanced androids coordinate with other automated systems - as demonstrated in Chinese factories where humanoids work alongside autonomous forklifts and logistics robots, creating integrated workflows .
Challenges in Realizing the Android Future
Despite rapid progress, significant hurdles remain in perfecting In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android:
Technical Limitations
Power density remains problematic - high-performance actuators enabling human-like mobility require substantial energy, creating operational duration constraints. Current models average just 4-8 hours per charge depending on workload intensity.
Cognitive Development Barriers
While movement capabilities advance rapidly, true contextual reasoning and social intelligence development lags. Creating machines that understand nuanced human communication remains artificial intelligence's grand challenge.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Industry analysts note China's heavy dependence on imported high-performance chips and proprietary algorithms , creating strategic vulnerabilities as geopolitical tensions impact technology transfers.
Safety Imperatives
As human-robot interaction increases, safety becomes paramount. Incidents like the 2021 Tesla factory injury highlight risks when sophisticated machines operate near humans without fail-proof safety protocols .
Frequently Asked Questions: In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android
What's the difference between an android and a standard robot?
When examining In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android, the key distinction lies in biomimicry. Standard robots (like industrial arms) prioritize functional efficiency over human resemblance. Androids deliberately replicate human physiology and behavior to operate seamlessly in human environments using existing infrastructure like stairs, tools, and vehicles .
Can current androids experience emotions or consciousness?
No. Despite advanced emotional recognition algorithms enabling appropriate responses, androids possess no subjective experience or consciousness. They simulate emotional intelligence through sophisticated programming without actual feelings. The 2001 MIT "emotional robot" demonstrated response patterns resembling emotion, not authentic emotional states .
When might androids become common in households?
Industry analysts project significant consumer adoption around 2030, when costs should decrease from current $100,000+ prototypes to under $30,000 for functional models. Current pilots in elder care facilities (notably in Japan and China) will gradually expand to residential settings as capabilities improve and prices drop .
The Android Future Is Arriving Faster Than Expected
What seemed like science fiction just a decade ago is materializing in laboratories and factories worldwide. The question In Robotics What Is Meant By An Android now describes not hypothetical machines but real technologies entering service across industries. With China's market projected to grow 100-fold by 2035 and global investment surging, these human-like machines represent robotics' next evolutionary leap .
As android capabilities accelerate through AI integration, they promise to transform everything from manufacturing workflows to eldercare. Their unique value proposition lies in operating within human environments without costly retrofitting - climbing our stairs, using our tools, and eventually understanding our needs with emotional intelligence. This represents not replacement but augmentation, creating collaborative human-machine ecosystems that enhance capabilities rather than simply automating tasks.