In the realm of artificial intelligence and robotics, few creations capture the imagination quite like a robot that is like a human. These machines, designed to resemble and mimic human beings, have transitioned from science fiction to real-world applications. But why do robot that is like a human exist? What purpose do they serve, and what does the future hold? This article explores the reasons behind their development, their current applications, and their potential to shape our world. For more insights into AI and robotics, visit our Homepage.
A Brief History of Humanoid Robot That is Like A Human
The idea of a robot that is like a human is not new. As early as the 13th century, Muslim engineer Ismail al-Jazari created humanoid automata, such as a drink-serving robot. In the Renaissance, Leonardo da Vinci sketched a mechanical knight, a precursor to modern robotics. By the 20th century, advancements led to robots like Honda’s ASIMO, one of the first widely recognized robot that is like a human, capable of walking and interacting with environments.
Why Do Robot That is Like A Human Exists?
The development of a robot that is like a human is driven by several key factors, each addressing unique technological and societal needs:
Advancing Technology and Research: Creating a robot that is like a human pushes the boundaries of robotics and AI. These robots serve as testbeds for innovations in bipedal locomotion, dexterity, and cognitive processing, advancing our understanding of both machines and human capabilities.
Practical Applications in Human Environments: Their human-like form allows them to operate in spaces designed for humans, such as homes, offices, or factories. They can use tools and navigate environments without requiring significant modifications.
Enhancing Human-Robot Interaction: A robot that is like a human can interact more naturally with people, making them suitable for roles in customer service, education, or companionship. Their familiar appearance reduces the learning curve for human interaction.
Addressing Labor Shortages: With aging populations and labor shortages in industries like manufacturing and healthcare, a robot that is like a human can perform repetitive or hazardous tasks, filling critical gaps in the workforce.
Supporting Scientific Research: These robots aid in studying human movement, cognition, and social behavior, contributing to fields like neuroscience and psychology.
Notable Examples of Humanoid Robots
Several robot that is like a human have made significant impacts across various sectors. Here are some prominent examples:
| Robot | Developer | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sophia | Hanson Robotics | Human-like appearance, conversational AI | Media, education, customer service |
| Atlas | Boston Dynamics | Agility, strength, parkour capabilities | Manufacturing, logistics, search and rescue |
| Pepper | SoftBank Robotics | Emotion recognition, interactive design | Retail, hospitality, customer service |
| ASIMO | Honda | Bipedal walking, environmental interaction | Research, public demonstrations (retired) |
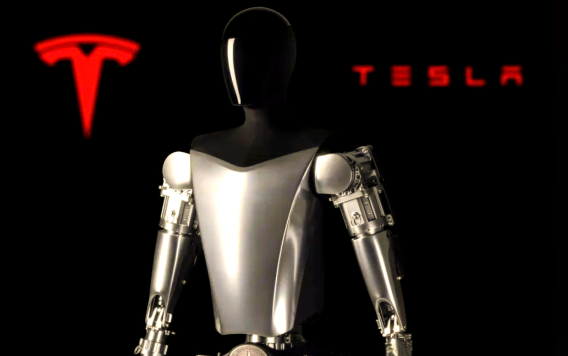
| Optimus | Tesla | AI-driven, human-like dexterity | Manufacturing, future household tasks |
Applications Across Industries
A robot that is like a human is transforming industries by leveraging their unique capabilities:
Healthcare: Robots like Pepper assist with patient care, reminding patients to take medications or providing companionship to the elderly.
Manufacturing: Atlas and Optimus handle repetitive or dangerous tasks, such as material handling or assembly, improving efficiency and safety.
Retail and Hospitality: Robots like Pepper enhance customer experiences by providing information and assistance in stores or hotels.
Education: Humanoid robots aid in teaching, particularly for children with special needs, by offering interactive learning experiences.
Entertainment: Robots like ALTER 3, developed by Osaka University, perform in theaters or conduct orchestras, blending technology with art.
Future Prospects of Robot That is Like A Human
The future of a robot that is like a human is promising, with several trends shaping their development:
Market Expansion: The global market for humanoid robots is projected to reach $38 billion by 2035, driven by advancements in AI and cost reductions ([Goldman Sachs](https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/articles/the-global-market-for-robots-could-reach-38-billion-by-2035)).
Technological Advancements: Improvements in AI, such as natural language processing and computer vision, are enhancing autonomy and interaction capabilities. Cheaper components and better manufacturing techniques are also reducing costs.
Commercial Viability: Companies like Tesla and Boston Dynamics are scaling production, with robots like Optimus expected to enter factories soon.
Global Competition: Countries like the US and China are racing to lead in humanoid robotics, with significant investments fueling innovation.
Societal Impacts of Humanoid Robots
The integration of a robot that is like a human into society will have far-reaching effects:
Economic Impact: These robots can boost productivity and create new industries but may displace low-skill jobs, necessitating retraining programs.
Social Impact: They offer companionship and support, particularly for the elderly, but raise concerns about privacy and the nature of human relationships.
Ethical Considerations: Questions about robot rights, accountability, and the moral implications of human-like machines require careful consideration.
Challenges in Robot That is Like A Human Development
Despite their potential, developing a robot that is like a human faces several hurdles:
Technical Challenges: Achieving stable bipedal movement, dexterous hands, and advanced AI remains complex.
Cost: While costs are decreasing, high-end models can still range from $30,000 to $150,000 ([Goldman Sachs](https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/articles/the-global-market-for-robots-could-reach-38-billion-by-2035)).
Safety: Ensuring safe interactions with humans is critical, as their strength and autonomy could pose risks if not properly managed.
FAQs
1. What is a Robot That is Like A Human?
A robot that is like a human is designed to resemble the human body, typically with a torso, head, arms, and legs. Equipped with AI and sensors, it mimics human movements and interactions for tasks in human environments.
2. How do humanoid robots differ from other robots?
Unlike specialized robots with specific forms, a robot that is like a human has a human-like appearance and versatile capabilities, enabling intuitive interactions and operation in human-designed spaces.
3. What are the main challenges in developing humanoid robots?
Key challenges include achieving stable bipedal locomotion, developing dexterous hands, integrating advanced AI, and ensuring safe human interactions, all while managing high development costs.
4. Can humanoid robots replace human workers?
A robot that is like a human can augment human work by handling repetitive or dangerous tasks, but they are unlikely to fully replace humans, instead enabling focus on creative or complex roles.
5. Which industries benefit most from humanoid robots?
Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, retail, hospitality, and education benefit significantly, with applications ranging from assembly line work to patient care and customer service.
Conclusion
A robot that is like a human represents a remarkable fusion of technology and human ingenuity. They exist to advance scientific discovery, address practical needs, and enhance human interactions. From assisting in factories to providing companionship, their applications are vast and growing. As technology progresses, the potential of a robot that is like a human to transform industries and daily life is immense, but it comes with the responsibility to address ethical, social, and economic challenges. By developing these robots thoughtfully, we can ensure they amplify human potential while fostering a harmonious coexistence.