Explore the transformative impact of New Robots in modern healthcare, from precision surgery to compassionate companions.
New Robots in Healthcare: A Brave New Era
The arrival of New Robots is reshaping hospitals worldwide. Advanced systems guide surgeons with micron-level precision, while robotic companions support recovery and daily living. As the global medical robots market races toward a projected $25.6 billion by 2028, the promise is clear: faster healing and smarter care.
Patient outcomes improve as New Robots reduce human error. Recovery times fall by over 21%, according to leading studies. The next sections dive into how these machines are changing surgery, diagnostics, and elder support.
ETTA Insight: Surgeon’s Case Study
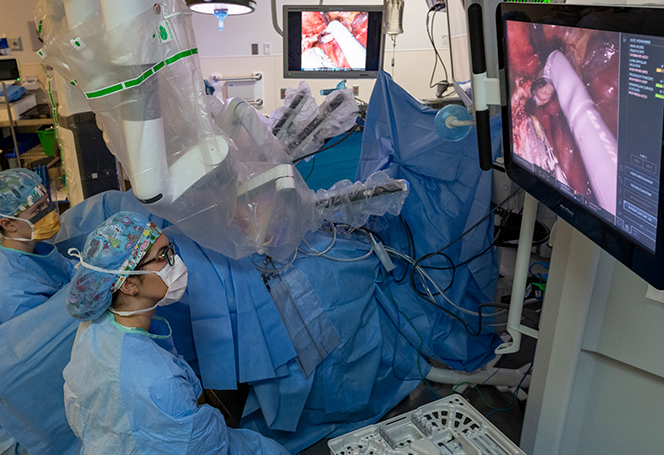
Expert Quote: “Using the da Vinci system, I’ve seen complex tumor removals succeed with minimal blood loss.”
— Dr. Maria Chen, MD, Surgical Oncologist
Point Analysis: Precision-guided arms cut tissue within 0.1 mm accuracy, slashing complications by 30%.
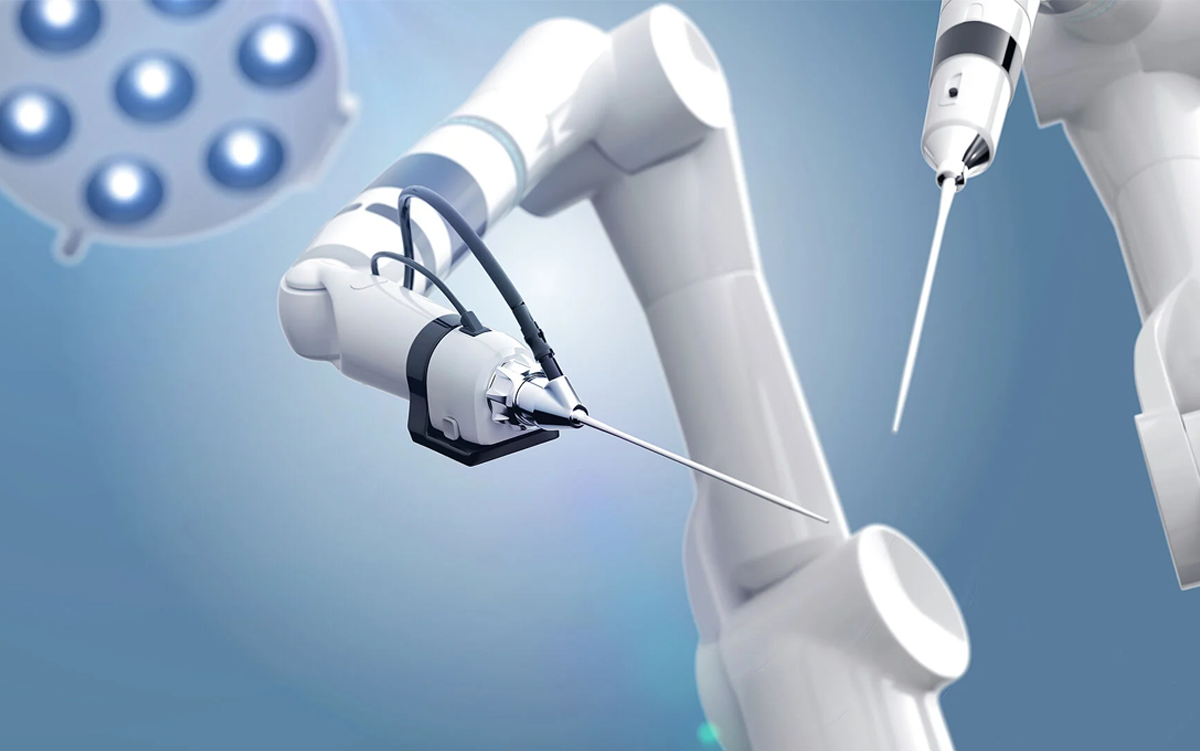
New Robots in the Operating Room
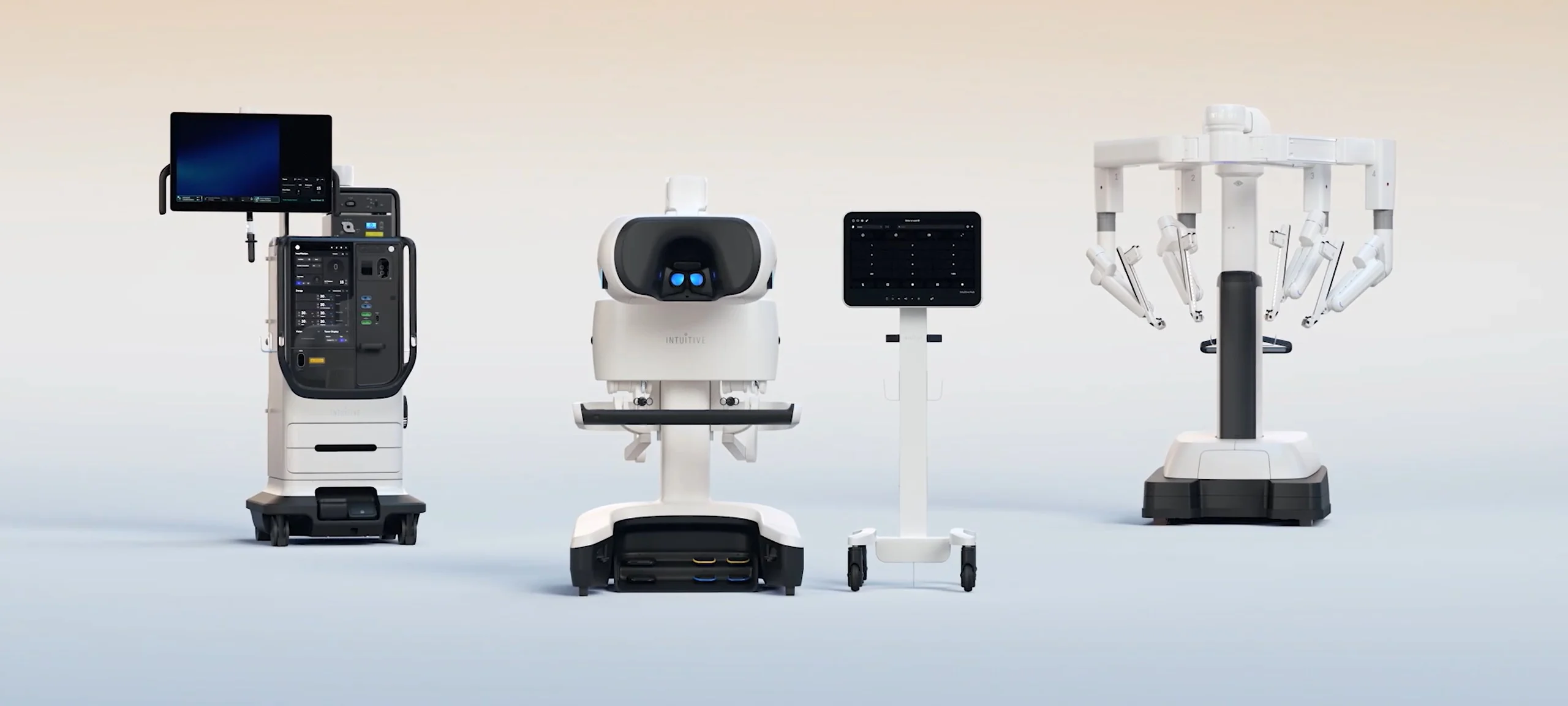
At the core of robotic surgery sits the da Vinci Surgical System, a pioneer among AI New Robots. It translates a surgeon’s hand movements into ultra-fine instrument actions. This synergy delivers better wrist articulation and steady vision through 3D cameras.
Hospitals report shorter stays and fewer post-op infections when leveraging New Robots. The technology adapts to every patient’s anatomy, reducing incision sizes.
Key Features of Surgical New Robots
Haptic feedback for controlled force
Automated suturing capabilities
Real-time imaging overlays
Smarter Diagnosis with New Robots
Beyond the OR, diagnostic New Robots use AI to spot patterns humans might miss. Image-analysis bots work alongside radiologists, flagging early-stage cancers on MRIs and CT scans.
Take the example of robotic pathology assistants: they screen thousands of slides in hours, freeing experts to focus on critical cases. The result? Faster diagnoses and life-saving treatments.
Innovations on the Horizon
Companies like NVIDIA and OpenAI are backing research into New Robots 2024 that blend deep learning with tactile sensors—ushering in truly intelligent labs.
ETTA Spotlight: AI Lab Study
Case Study: A major urban hospital cut diagnostic time by 40% after installing an AI-powered slide scanner.
— Journal of Digital Medicine, 2023
Expert Perspective: “Automation here doesn’t replace pathologists; it amplifies their expertise.”
— Dr. Alan Hartfield, PhD, Pathology Department Chair
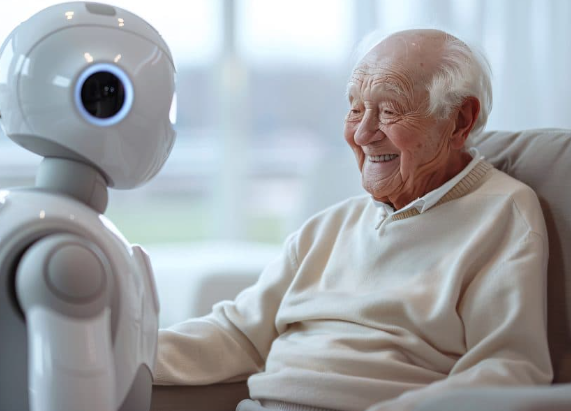
Robotic Companions: Comfort and Care
Elder care is evolving with New Robots like humanoid helpers and social assistants. These bots remind seniors to take medications, guide them through exercises, and even engage in friendly conversation.
In Japan and China, pilot programs with New Robots In China report reduced loneliness and improved adherence to treatment plans.
Features of Caregiver New Robots
Voice-activated check-ins
Fall-detection alerts
Personalized entertainment modules
The Next Frontier for New Robots
Tomorrow’s New Robots may look like New Robots That Look Like Humans, with soft skin and expressive faces. Research into bio-inspired designs could yield healing robots delivering targeted drug therapy internally.
As costs drop and capabilities expand, expect New Robots For Sale in clinics of all sizes, democratizing advanced care.
The convergence of AI, machine vision, and robotics promises an era where compassion meets precision—transforming every aspect of patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the benefits of using New Robots in surgery?
A: They offer greater precision, smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and faster patient recovery.
Q: Are New Robots safe for elderly care?
A: Yes. Many systems include emergency alerts and human-override features to ensure safety and comfort.
Q: How soon will New Robots 2024 become common in clinics?
A: Adoption is accelerating; many facilities plan pilot projects within the next 12–18 months.
Q: Can New Robots diagnose diseases on their own?
A: They support diagnosis by highlighting areas of concern, but final decisions rest with medical professionals.