The rise of the Robotic Car has sparked questions about how it differs from the autonomous vehicle. In this article, we’ll clarify key terms—robotic car, autonomous vehicle, automated vehicle, and driverless car—while exploring the six levels of automation defined by SAE. By the end, you’ll understand industry nuances and see real-world examples that prove these distinctions.
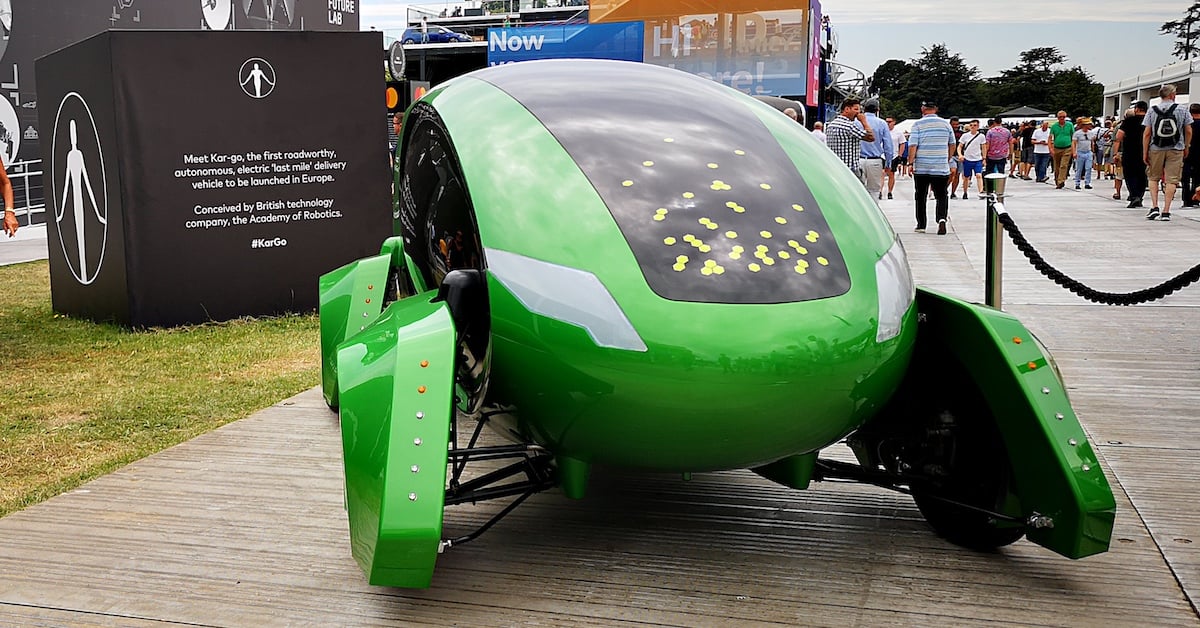
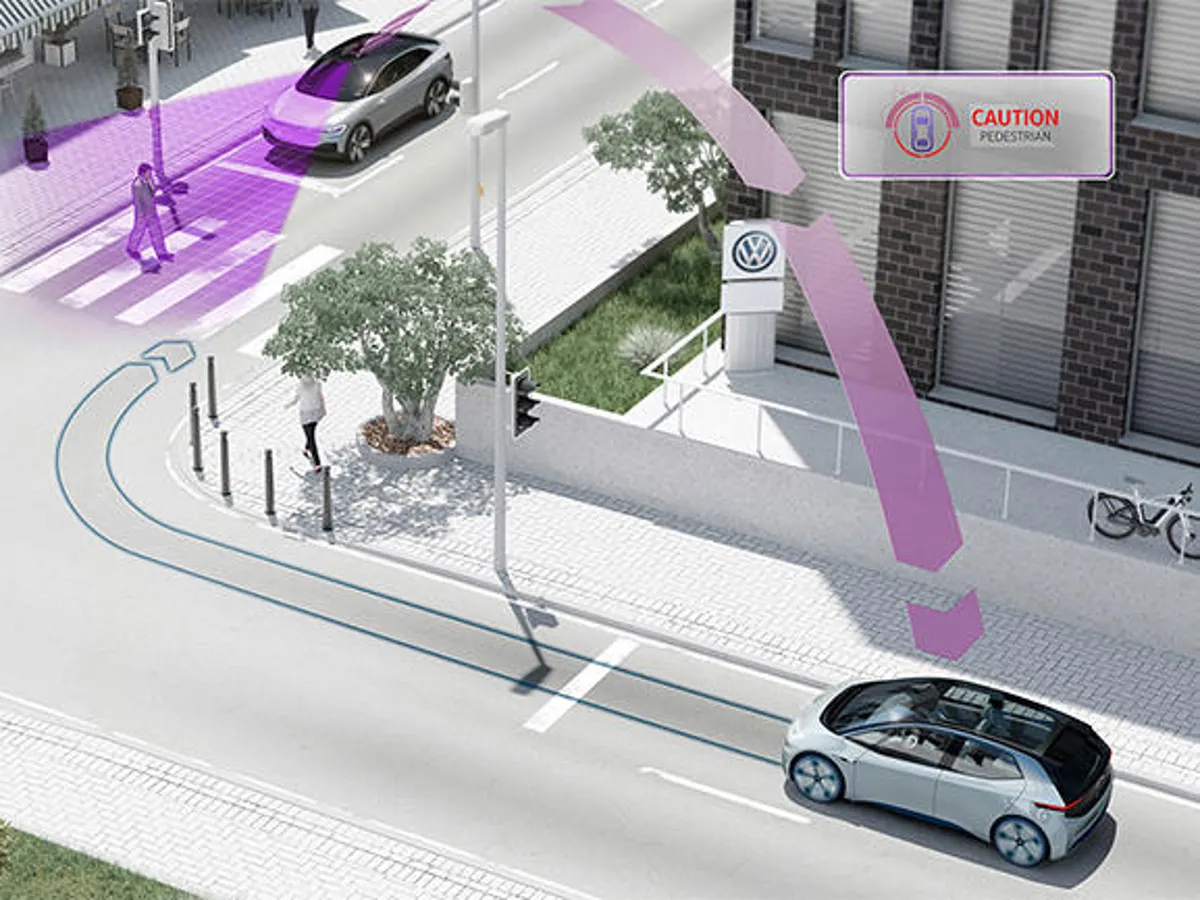
A robotic car is a vehicle equipped with sensors, actuators, and control systems to perform driving tasks without human input. An autonomous vehicle uses advanced algorithms and environmental data to navigate complex roads. An automated vehicle emphasizes the system’s role over the human driver. Meanwhile, a driverless car operates without any onboard human driver. Regulatory bodies prefer precise terminology. For instance, NHTSA favors the term “Automated Driving Systems” over “autonomous.” Understanding these labels helps distinguish between a simple robotic car wash unit and a full-scale self-driving car project. An automated vehicle performs specific driving tasks like parking or lane keeping. It often requires a fallback-ready human driver. Examples include systems found in today’s production cars offering automatic braking or cruise control. An autonomous vehicle handles all driving functions under certain conditions, without human intervention. These vehicles rely on LIDAR, radar, cameras, and AI to interpret their environment, similar to a robotic car parking system but on a larger scale. Driverless cars remove the human from the driver’s seat entirely. Meanwhile, “robotic” emphasizes the mechanical and programmable aspect common to projects like an Arduino Robotic Car hobby kit or a full-scale Tesla experiment. SAE defines levels from 0 (no automation) to 5 (full automation). Most modern cars sit at Level 2, offering combined steering and acceleration but requiring human oversight. Level 3 allows conditional autonomy, while Level 4 and 5 approach true driverless status. Here’s a quick breakdown: Level 0: No Automation Level 1: Driver Assistance (e.g., adaptive cruise control) Level 2: Partial Automation (e.g., lane centering + adaptive cruise) Level 3: Conditional Automation Level 4: High Automation (geofenced autonomy) Level 5: Full Automation (all conditions) Projects like the robotic car project at MIT focus on pushing from Level 2 to Level 4 by testing in controlled environments. Beyond consumer vehicles, robotic systems serve in maintenance and services. For instance, a robotic car wash machine price can range from $20,000 to $100,000 depending on capacity. Similarly, automated robotic car washing machine setups reduce labor costs and improve consistency. Education kits like the robotics car kit help students learn programming and electronics. DIY guides on how to make a robotic car often use Arduino boards, ultrasonic sensors, and motor drivers. Meanwhile, toy enthusiasts enjoy building a robot car toy to explore simple AI principles. 1. What makes a Robotic Car different from a self-driving car? A Robotic Car highlights programmable robotics components, while “self-driving” focuses on AI-driven navigation without human input. 2. Can I find a robotic car wash near me? Yes, many urban areas offer automated robotic car wash services that operate without attendants. 3. Is the robotic car parking feature available in consumer cars? Several modern models include automated parking assistance, often branded as “Park Assist” or “Auto Park.” 4. How much does a basic robotic car project pdf guide cost? Many online PDFs are free or under $50, covering step-by-step assembly and coding instructions. Understanding the distinctions between a Robotic Car, autonomous vehicle, automated vehicle, and driverless car is key for consumers and industry watchers. Terms may overlap, but regulations and safety guidelines depend on clear definitions. As technology advances from SAE Level 2 to Level 5, we’ll see more real-world robotic car applications—from advanced robotic car wash terdekat stations to fully driverless shuttles. Stay informed about terminology and system capabilities to navigate this evolving landscape.Defining the Robotic Car and Related Terms
Industry Definitions: Automated Vehicle vs. Autonomous Vehicle
Automated Vehicle
Autonomous Vehicle
SAE’s Six Levels of Automation
Real-World Applications
FAQs
Conclusion