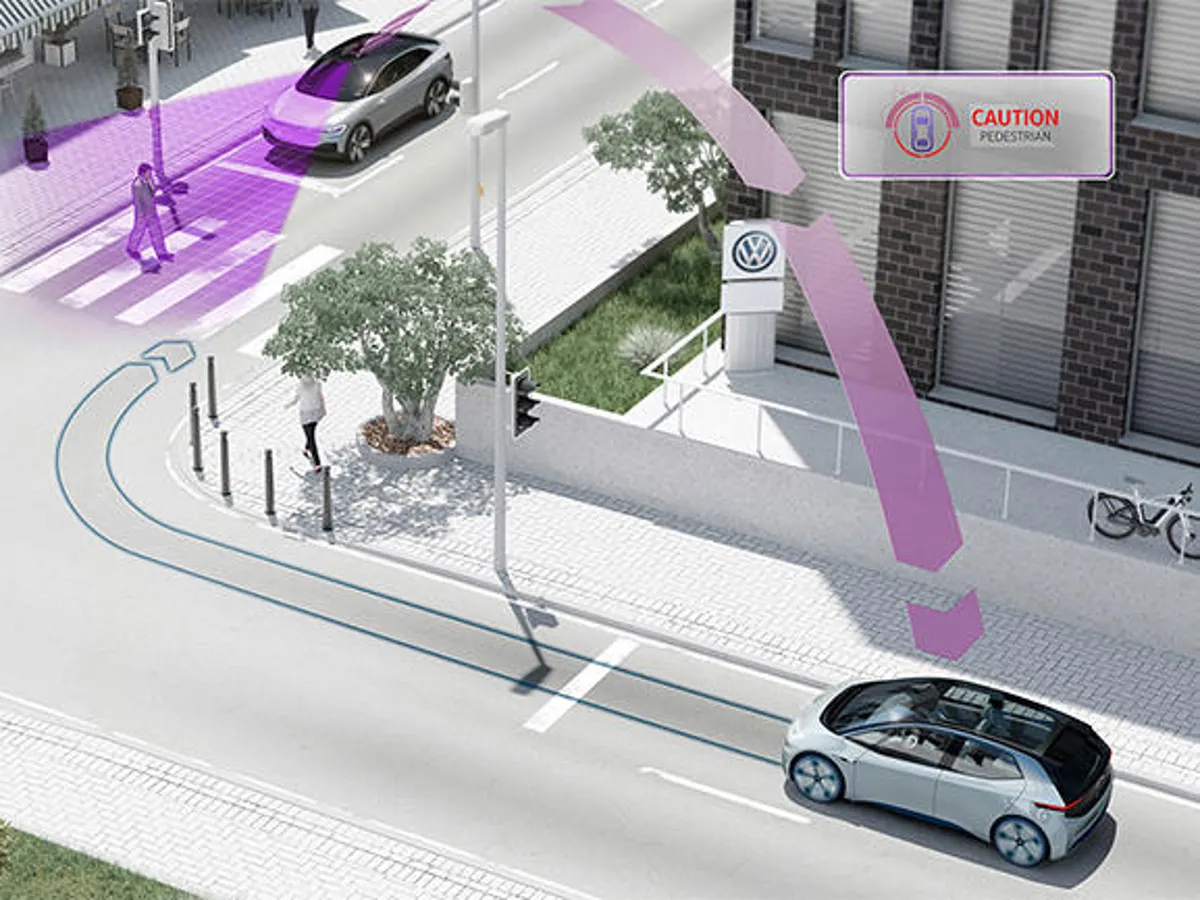
The journey of the Robotic Car has reshaped how we think about mobility. Starting from academic experiments, today’s driverless fleets redefine city travel. This article traces milestones from the DARPA Grand Challenges to modern robotaxis.
In 2004, DARPA launched the Grand Challenge to spur development of autonomous ground vehicles. Teams like Stanford’s “Stanley” tackled a 142-mile desert course. The 2005 rerun saw five finishers, proving viability. By 2007, the third DARPA challenge included urban settings. Vehicles navigated traffic, signs, and curves. This leap pushed the Robotic Car closer to real-world use.From DARPA to Dawn of the Robotic Car
Expert Insight
“The DARPA challenges demonstrated that autonomy was no longer science fiction,” says Dr. Elena Rodriguez, AI researcher at Tech University.
In 2014, Tesla introduced Autopilot, the first mass-market advanced driver assist. Over 3 billion miles have been driven under its guidance. This technology bridged consumer vehicles and true autonomy. Soon, third-party developers offered robotic car project kits for enthusiasts. DIY makers explored how to make a robotic car using robot car kit components. Arduino boards powered simple models, inspiring future engineers. Others searched for robotic car wash machines or compared robotic car wash machine price tags. Even local garages advertised robotic car parking systems near busy malls.The Rise of Tesla and the Robotic Car Autopilot
Hobbyists and the Robotic Car
Case Study
Waymo’s pilot in Phoenix logged over 20 million miles by 2022. Their fleet of 600 robotaxis served thousands of riders weekly.
In 2009, Google began testing self-driving prototypes on public roads. Early vehicles achieved Level 3 autonomy under controlled conditions. By 2016, the program spun off into Waymo, focusing solely on robotaxi services. Their Fremont factory churned out modified SUVs ready for testing. Cruise linked with General Motors to deploy over 1,000 driverless vehicles in San Francisco. Passengers hail cars via app, enjoying zero-emission travel. Meanwhile, competitors like Pony.ai and Mobileye join the race. The global Robotic Car market is projected to exceed $60 billion by 2028. New ventures combine healthcare and autonomy: robotic cardiac surgery robots assist surgeons with precision. Educational programs now include robotics car kit courses. Children play with robot car toy models that mimic full-scale functions, sparking early STEM interest.Google’s Self-Driving Prototypes and the Robotic Car Boom
Cruise, Waymo, and Today’s Robotic Car Fleets
Innovation Beyond Transport
Point Analysis
Safety gains: 90% fewer accidents in test zones.
Economic impact: over 50,000 new jobs in autonomous tech.
Consumer trust: surveys show 70% willingness to ride robotaxis.
From DARPA’s deserts to city streets, the Robotic Car has evolved rapidly. Tesla’s Autopilot paved the way, while Waymo and Cruise operate fleets today. Innovators continue exploring new applications in washing, parking, and even surgery. The road ahead promises smarter, safer, and more sustainable travel. A Robotic Car is a vehicle capable of navigating and driving itself using sensors, AI, and mapping data. It ranges from Level 2 Driver Assist to Level 5 Full Autonomy. In controlled pilot programs, Robotic Cars have shown a 90% reduction in accidents compared to human drivers. They follow strict safety protocols and real-time obstacle detection. Yes. Hobbyists use robot car kit or follow robotic car project pdf guides online. Tools like Arduino and Raspberry Pi simplify prototyping. Prices vary by city. Robotaxi rides often match ride-share rates but may include dynamic pricing. Installation of home robotic car washing machine systems ranges from $5,000 to $15,000.Conclusion: The Future of the Robotic Car
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Robotic Car?
How safe are today’s Robotic Car fleets?
Can I build my own Robotic Car?
What’s the cost of Robotic Car services?