Space robots are the unsung heroes of cosmic exploration, performing tasks too dangerous or impossible for humans. From Martian rovers analyzing soil samples to robotic arms assembling space stations, these mechanical marvels are our eyes, hands, and tools in the void. What Do Space Robots Do exactly? They revolutionize exploration, conduct precise scientific experiments, maintain spacecraft, and pave the way for human expansion into the solar system. This article reveals their fascinating roles beyond what you see in movies.
Article Structure
The Evolution of Space Robotics
Primary Functions of Space Robots
Famous Space Robots and Their Missions
Future Applications of Space Robotics
FAQs About Space Robots
The Evolution of Space Robotics: From Simple Tools to Autonomous Explorers
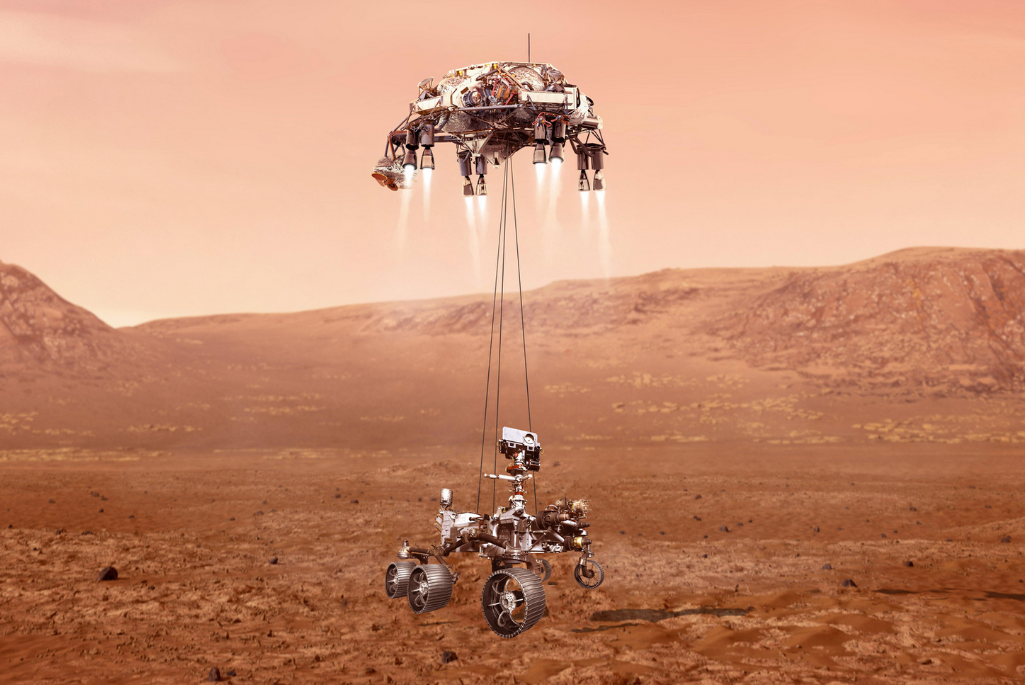

The history of space robotics began with simple mechanical arms on early spacecraft, evolving into today's sophisticated autonomous systems. The Soviet Union's Lunokhod 1 in 1970 was the first successful space robot, a rover that explored the Moon's surface for nearly a year. NASA's Viking landers in 1976 carried robotic arms that collected Martian soil samples, while the Space Shuttle's Canadarm demonstrated the value of robotic systems in orbital operations.
Modern space robots like NASA's Perseverance rover represent the cutting edge, equipped with AI for autonomous navigation and decision-making. The International Space Station's robotic systems, including Canadarm2 and Dextre, show how crucial robots have become for maintenance and operations in space. These systems have transformed our understanding of What Do Space Robots Do by expanding their capabilities far beyond initial expectations.
Future developments focus on increasing autonomy and versatility. Projects like ESA's PROBA-3 and NASA's OSAM-1 aim to demonstrate robotic satellite servicing, while concepts for lunar construction robots and asteroid mining systems push the boundaries of What Space Robots Can Do. The line between robotic tools and autonomous explorers continues to blur as technology advances.
Primary Functions: What Do Space Robots Do in Actual Missions?
1. Planetary Exploration and Surface Operations
Space robots excel at exploring planetary surfaces where humans cannot yet venture. Rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance analyze soil composition, search for signs of past life, and test technologies for future human missions. Their robotic arms contain sophisticated tools for drilling, scooping, and analyzing samples, while onboard laboratories perform experiments in situ.
Landers such as InSight study planetary interiors using robotic deployments of seismometers and heat probes. These missions answer fundamental questions about planetary formation and evolution, demonstrating What Space Robots Do to advance our scientific understanding. Future missions will deploy more advanced robotic systems, including flying drones like Mars Helicopter and potential submarine robots for icy moons.
Beyond science, space robots prepare for human arrival by testing resource utilization techniques. The upcoming Mars Sample Return mission will involve an unprecedented robotic collaboration between rovers, landers, and orbital systems to bring Martian samples to Earth, showcasing the growing complexity of What Space Robots Can Achieve.
2. Orbital Operations and Satellite Servicing
In Earth orbit, space robots perform delicate operations that would be dangerous or impossible for astronauts. The International Space Station's Canadarm2 has assembled station modules, captured visiting spacecraft, and assisted spacewalks. Its successor, Dextre, handles precise tasks like replacing orbital replacement units and conducting experiments.
Newer missions like Northrop Grumman's Mission Extension Vehicles demonstrate robotic satellite servicing, prolonging the life of valuable orbital assets. The upcoming OSAM-1 mission will attempt robotic refueling of satellites not designed for servicing, potentially revolutionizing space operations. These applications show What Space Robots Do to maintain and extend our orbital infrastructure.
Future orbital robotics may include assembly of large space telescopes, construction of orbital habitats, and even debris removal. Projects like ClearSpace-1 aim to demonstrate active debris removal using robotic capture systems, addressing the growing problem of space junk.
3. Deep Space Exploration and Sample Collection
Robotic probes venture where humans cannot yet go, exploring the outer solar system and beyond. NASA's Voyager probes, now in interstellar space, continue to send data decades after launch. More recent missions like New Horizons revealed Pluto's complexity, while Juno studies Jupiter's mysteries.
Sample return missions represent some of the most sophisticated examples of What Space Robots Do. Japan's Hayabusa2 successfully returned samples from asteroid Ryugu, while NASA's OSIRIS-REx collected material from Bennu. These missions require precise robotic operations millions of miles from Earth, with no possibility of human intervention if problems arise.
The future promises even more ambitious robotic explorers, including probes to study the ice giants Uranus and Neptune, and potential missions to explore the hypothesized Planet Nine. Each mission pushes the boundaries of What Space Robots Can Do in extreme environments.
Famous Space Robots and Their Groundbreaking Missions
Several iconic space robots have transformed our understanding of the cosmos. The Mars Exploration Rovers Spirit and Opportunity far exceeded their planned 90-day missions, with Opportunity operating for nearly 15 years. Their discoveries of evidence for past water activity reshaped our understanding of Mars' history.
The Hubble Space Telescope, while not mobile, contains sophisticated robotic systems for instrument changes and repairs. Its successor, the James Webb Space Telescope, features even more advanced robotic mechanisms for its complex deployment sequence. These observatories demonstrate What Space Robots Do to expand our view of the universe.
Less known but equally impressive are robots like ESA's Philae lander, which made the first controlled touchdown on a comet despite harpoon failure. NASA's InSight lander deployed the first robotic mole on Mars to study planetary heat flow. Each mission expands the repertoire of What Space Robots Can Accomplish in diverse environments.
The Future of Space Robotics: What's Next?
Emerging technologies promise to revolutionize What Space Robots Do in coming decades. Swarm robotics concepts envision dozens of small robots working together on planetary surfaces, while bio-inspired designs may create robots that crawl, hop, or even slither across alien terrain. NASA's Shapeshifter concept envisions a collective of robots that can combine into different configurations for various tasks.
Artificial intelligence will enable greater autonomy, allowing robots to make complex decisions without waiting for commands from Earth. This is crucial for operations around distant worlds where light-speed delays make real-time control impossible. Future lunar robots may construct habitats using locally sourced materials before human crews arrive.
The ultimate test of space robotics may come with interstellar missions. Concepts like Breakthrough Starshot envision tiny robotic probes traveling to nearby stars, while more conventional designs might carry out centuries-long voyages to explore distant planetary systems. These missions would push the boundaries of What Space Robots Can Do beyond anything attempted before.
FAQ 1: What Was the First Space Robot?
The first operational space robot was the Soviet Union's Lunokhod 1, which landed on the Moon in November 1970. This robotic rover operated for 322 Earth days, traveling over 10 km while transmitting thousands of TV images and hundreds of high-resolution panoramas. It pioneered many technologies that later space robots would build upon.
FAQ 2: How Do Space Robots Survive Extreme Conditions?
Space robots are engineered to withstand conditions that would destroy most electronics. They use radiation-hardened components, thermal control systems (heaters and radiators), and redundant systems for critical functions. Martian rovers, for example, survive temperatures from -130°C to +30°C using radioisotope heaters and carefully managed power systems.
FAQ 3: Can Space Robots Repair Themselves?
While current space robots have limited self-repair capabilities, future systems may incorporate more advanced autonomous repair technologies. The Mars rovers have occasionally used creative methods to overcome problems, like Spirit driving backward to compensate for a stuck wheel. NASA is developing technologies for self-repairing electronics and self-healing materials that could revolutionize What Space Robots Can Do in the future.
Conclusion: The Expanding Universe of Space Robotics
From humble beginnings as simple mechanical arms, space robots have evolved into sophisticated explorers that transform our understanding of the cosmos. What Do Space Robots Do? They extend human presence throughout the solar system, conduct precise scientific investigations, maintain critical orbital infrastructure, and pave the way for future human expansion. As technology advances, these robotic pioneers will take on even more ambitious roles, from constructing lunar bases to potentially traveling to other stars.
The next decade promises revolutionary developments in space robotics, with missions to return Martian samples, explore ocean worlds, and demonstrate orbital manufacturing. Each mission expands our understanding of What Space Robots Can Do while inspiring new generations of engineers and scientists. As we stand on the brink of a new era in space exploration, robots will continue to be our indispensable partners in unlocking the mysteries of the universe.