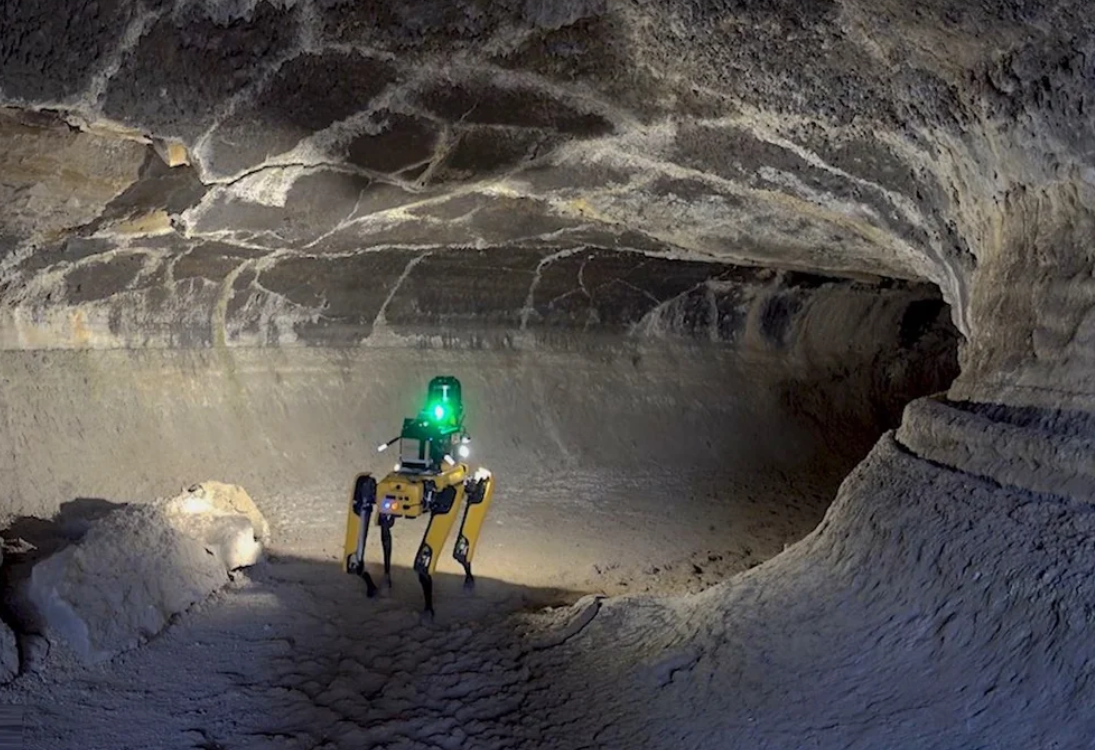
Summary: This article explores the smart strategies top Robot Companies use to train AI systems that work in the unpredictable physical world. From Reinforcement Learning to digital twins, discover how companies reduce error rates by up to 60% while building intelligent machines of the future.
As demand for autonomous systems rises, Robot Companies face mounting pressure to ensure their AI agents perform accurately in complex, unpredictable environments. Training AI in purely virtual conditions often results in systems that fail when facing physical world constraints—such as friction, sensor noise, or real-time human interaction. Today’s Robot Companies need scalable, low-risk solutions to prepare robots for these challenges. This is where cutting-edge training techniques like sim-to-real transfer, digital twins, and Reinforcement Learning step in, narrowing the gap between simulation and reality. Reinforcement Learning allows AI to learn through experience—just like humans. An AI agent is placed in a virtual environment, performs actions, and receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. Through millions of iterations, it refines its decision-making. Robot Companies like Agility Robotics and NVIDIA leverage this technique to enable robots to grasp objects, navigate terrain, and recover from falls. By learning in simulation first, the risk to hardware is minimized. This approach involves training robots in a virtual replica of the real world. Simulations can mimic lighting conditions, terrain roughness, sensor latency, and even battery decay. These variations make the AI robust to change and unpredictability. According to internal testing by several Autonomous Robot Companies, sim-to-real training has cut real-world deployment errors by up to 60%. This has become a cornerstone for almost every next-gen robotics startup and enterprise.The Real-World Challenge for Robot Companies
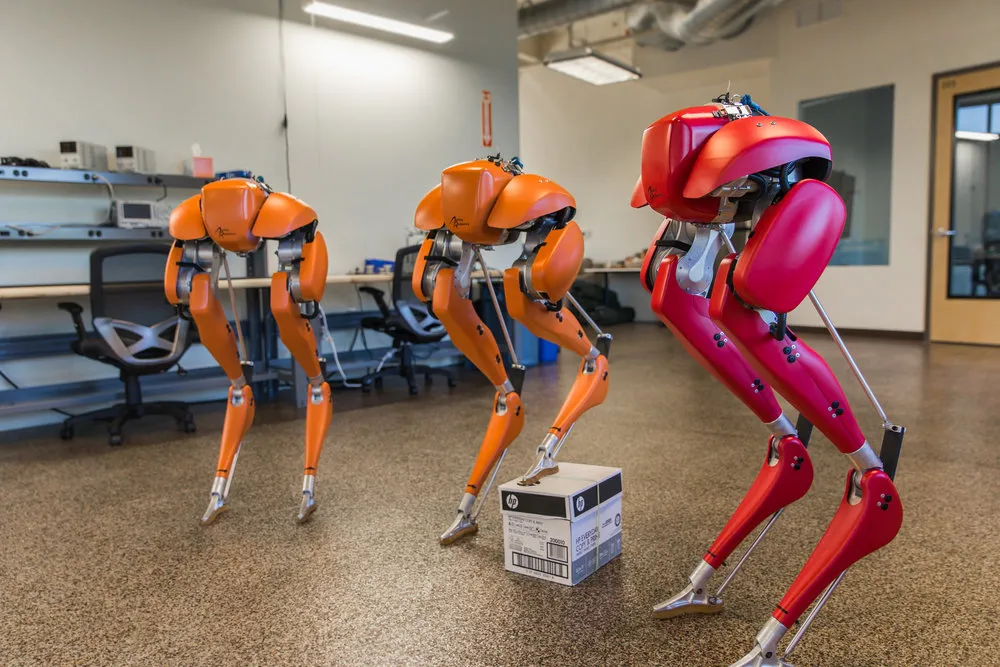

Core Training Strategies
Reinforcement Learning in Robotics
Sim-to-Real Transfer
Expert Insight
“Bridging simulation and the physical world is no longer optional—it’s the standard,” says Dr. Elena Garcia, AI Director at a top Humanoid Robot Company.
Highlight Fact
Over 90% of industrial Robot Companies now incorporate digital twins into their AI training pipelines (2024 industry analysis).
Digital twins are high-fidelity replicas of physical robots that run in parallel to real-world machines. They simulate how hardware would respond in various situations, allowing engineers to test, tweak, and optimize—without damaging anything. Boston Dynamics uses digital twins to simulate warehouse environments, slippery floors, and narrow corridors. Their robots, trained on thousands of scenarios, walk seamlessly over ice and gravel during actual deployments. Even with accurate simulations, there are discrepancies. To tackle this, Robot Companies apply "domain randomization"—a process where random visual and physical parameters are changed continuously during training. This helps the AI generalize and remain resilient. Instead of learning fixed rules, the robot learns adaptable strategies that work under any lighting, surface, or weather condition. Training simulations are run on powerful GPU clusters. Companies run millions of episodes in parallel. Each round improves the AI's accuracy, robustness, and efficiency. This makes training pipelines incredibly efficient and scalable for large fleets.Digital Twins: The AI Mirror
Case Study: Boston Dynamics
Bridging the Gap with Realistic Simulations
Massive Infrastructure Support
Agility Robotics Results
Their humanoid robot “Digit” went through over 200,000 virtual test walks before stepping into a real logistics center. Result: a 50% reduction in balance-related failures in early field tests.
Choosing the right simulation partner or training consultancy can make or break a deployment. Most Robot Companies now evaluate partners based on the following: Accuracy and fidelity of simulation tools Integration with hardware systems Scalability of training pipelines Support and maintenance experience Looking ahead, we’ll see AI models trained not just in virtual worlds, but through self-supervised learning and meta-learning techniques. AI will begin learning across multiple domains and continually improve after every deployment. Photorealistic game engines and real-time 3D sensors will further close the reality gap. As AI matures, so will the training pipelines used by Robot Companies—bringing us ever closer to fully autonomous, reliable machines. Training AI for the real world is no small feat. It demands a smart blend of simulation, real-world testing, digital twins, and Reinforcement Learning. Robot Companies that embrace these strategies are setting the standard for safe, scalable, and effective AI integration in robotics. As these tools evolve, the robots they produce will become ever more adaptable, autonomous, and intelligent. A1: It’s a method where AI is trained in virtual environments before deployment in the physical world. It reduces the need for risky real-world testing. A2: Digital twins allow Robot Companies to simulate and debug robot behavior virtually, saving time and hardware wear. A3: Robot Companies like Agility Robotics, Boston Dynamics, and NVIDIA are pioneers in training robust, real-world-ready AI. A4: By altering simulation parameters like lighting, noise, or textures to teach AI flexibility and generalization.Partnering for Performance
The Future of Training in Robot Companies
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is sim-to-real learning?
Q2: Why are digital twins important?
Q3: Which companies lead in AI robotics training?
Q4: How is domain randomization used?