When was the first AI robot made? The answer to this question takes us on a journey back to the mid-20th century, to a time when the concept of artificial intelligence was still a distant dream. The creation of the first AI robot marked a groundbreaking achievement in the history of robotics and artificial intelligence. Let's explore the pivotal moment in AI history when the first AI robot was made and how it set the stage for the advanced AI robots we see today.
The Birth of AI Robotics: The First AI Robot

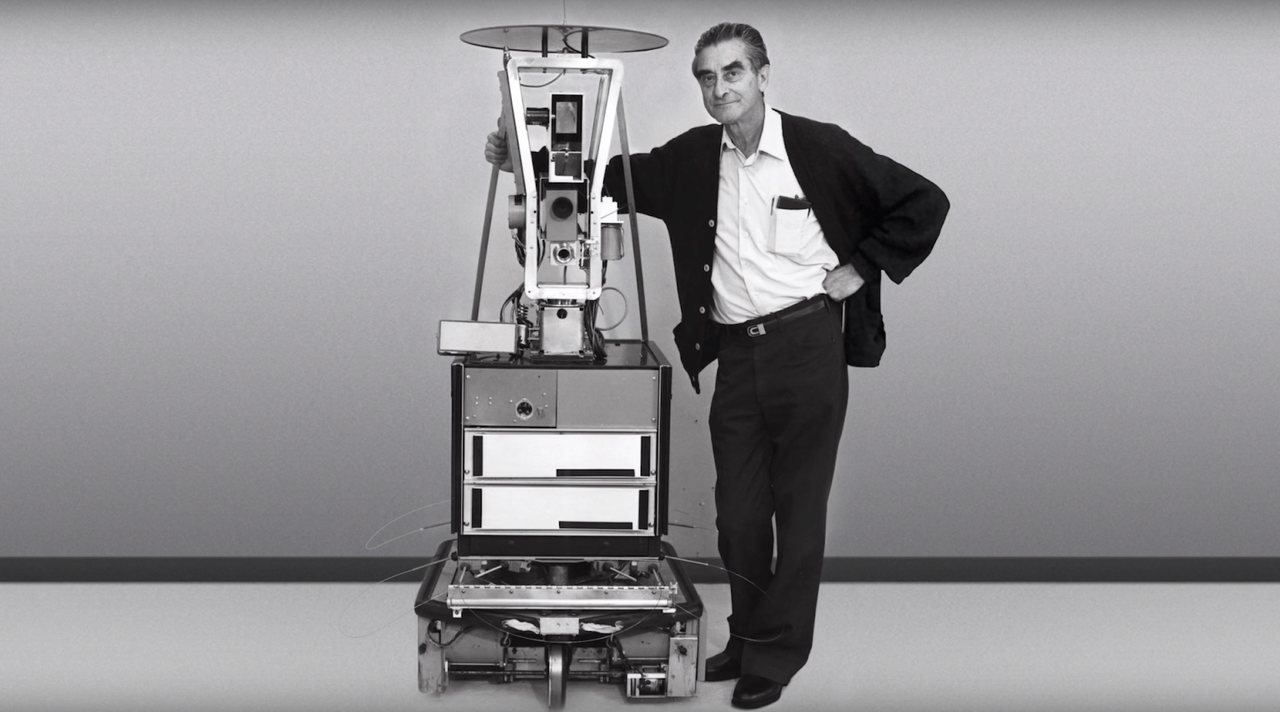
The first AI robot was not a futuristic, humanoid machine like the robots we see today, but rather a simple, yet revolutionary creation. In the early 1960s, researchers at the Stanford Research Institute (SRI) developed a robot named Shakey. Shakey was the first robot to exhibit artificial intelligence, making it a milestone in both AI and robotics. Its ability to perceive its environment, make decisions, and move autonomously was groundbreaking at the time.
Shakey was not fully autonomous like today's robots, but it represented a significant step forward. It used a basic form of AI called "reactive planning" to navigate its surroundings. The robot could interpret its environment using sensors, process the data, and take action based on its programming. This was a far cry from the fully autonomous robots like Sophia we see today, but it laid the groundwork for more advanced AI robots in the future.
AI Origins: The Foundation for Future Robotics
Shakey’s creation in 1966 was just the beginning. The development of Shakey provided essential insights into the challenges and potential of combining AI with robotics. Its ability to interact with its environment was a crucial step toward building intelligent robots. Shakey was one of the first robots to utilize AI algorithms for decision-making, showcasing the practical application of AI in machines.
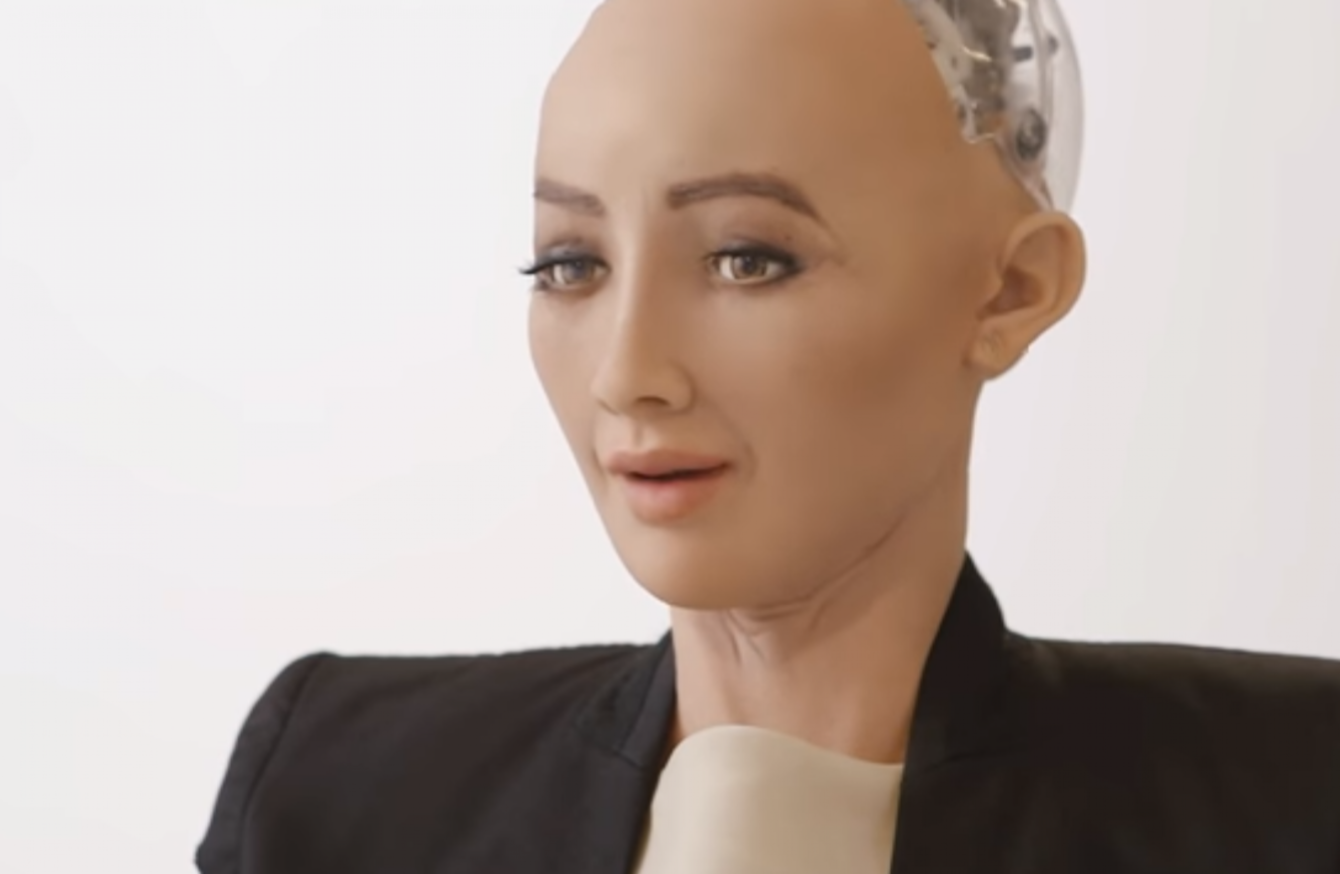
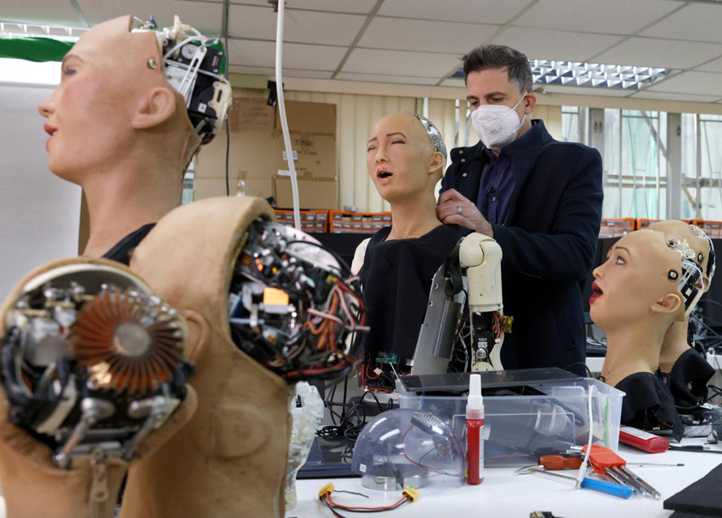
While Shakey was the first AI robot, it was far from perfect. It could only perform simple tasks like moving objects or avoiding obstacles. However, its creation sparked the development of future AI robots that could learn, adapt, and eventually perform much more complex tasks. This early work in AI robotics laid the foundation for the robots we see today, such as the famous humanoid robot, Sophia AI.
The Evolution of AI Robots: From Shakey to Sophia
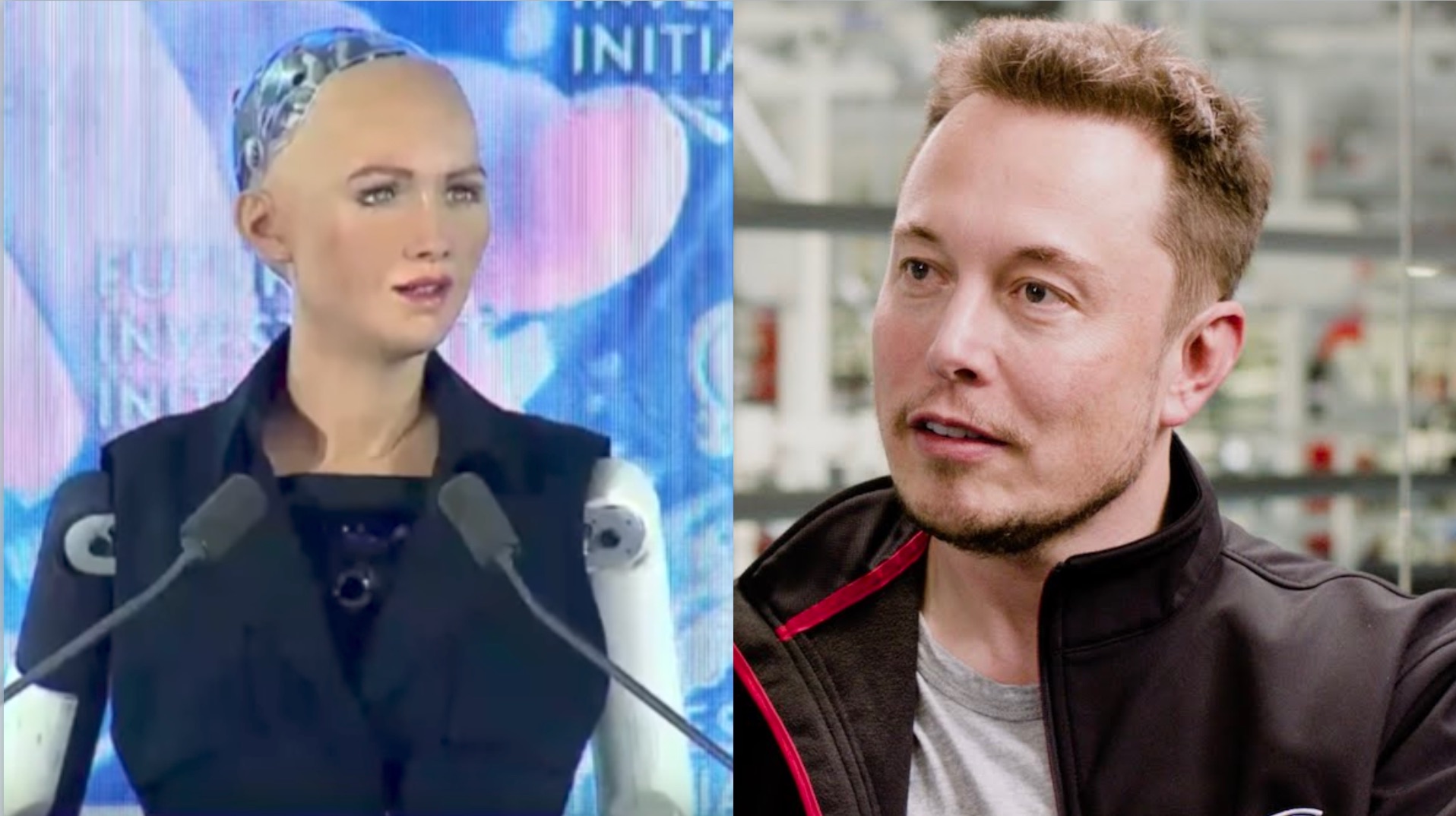
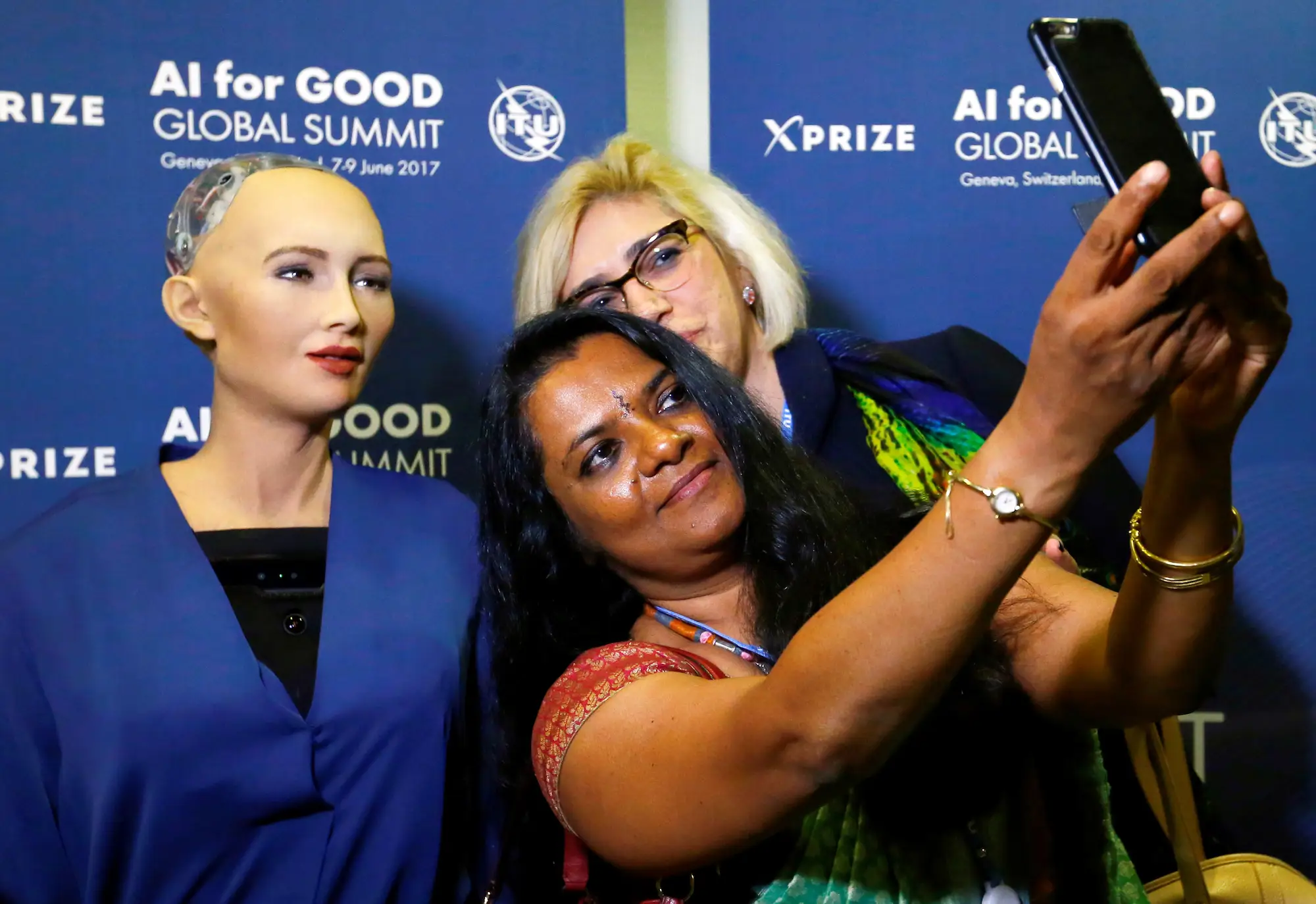
When was the first AI robot made? The answer, Shakey, represents a pivotal moment in AI history. However, the road from Shakey to modern AI robots like Sophia is a story of rapid evolution. As AI technology progressed, robots began to exhibit more advanced capabilities. Sophia, created by Hanson Robotics in 2016, is one of the most famous modern AI robots. Sophia can hold conversations, recognize faces, and express emotions—features that Shakey could never have dreamed of.
Despite the huge technological leap from Shakey to Sophia, the first AI robot's role in history cannot be overstated. Shakey’s development showed the world that AI could be integrated into robots, paving the way for future innovations in AI robotics.
The Significance of Shakey in AI and Robotics History
The creation of Shakey in 1966 marked a turning point in both the history of artificial intelligence and the development of robotics. While robots before Shakey were often mechanical devices designed for simple tasks, Shakey demonstrated that robots could be more than just machines—they could be intelligent systems capable of learning and adapting to their environments. This concept of robots with AI capabilities has become the standard in modern robotics, as seen with advanced robots like Sophia, who use AI to interact with humans and perform complex tasks.
Conclusion: Reflecting on the First AI Robot Made
When was the first AI robot made? The answer takes us back to Shakey, a simple yet revolutionary robot created in 1966. While Shakey wasn’t as advanced as the AI robots we see today, it played a crucial role in laying the groundwork for the AI robots that would follow. From its basic decision-making abilities to its influence on modern AI robots like Sophia, Shakey’s legacy is still felt in the world of AI and robotics today. The journey from Shakey to Sophia showcases just how far AI robots have come and gives us a glimpse of the exciting possibilities in the future of AI robotics.
FAQs: The First AI Robot and Its Legacy
1. What was the first AI robot?
The first AI robot was Shakey, developed by the Stanford Research Institute in 1966. It was the first robot to use AI algorithms to perceive its environment and make decisions.
2. Who created the first AI robot?
The first AI robot, Shakey, was created by a team of researchers at the Stanford Research Institute. Their work laid the foundation for future AI robots.
3. How has AI in robots evolved since Shakey?
Since Shakey, AI robots have become much more advanced, with robots like Sophia showcasing the ability to hold conversations, recognize faces, and express emotions. AI technology has evolved to include machine learning and deep learning, enabling robots to perform more complex tasks.