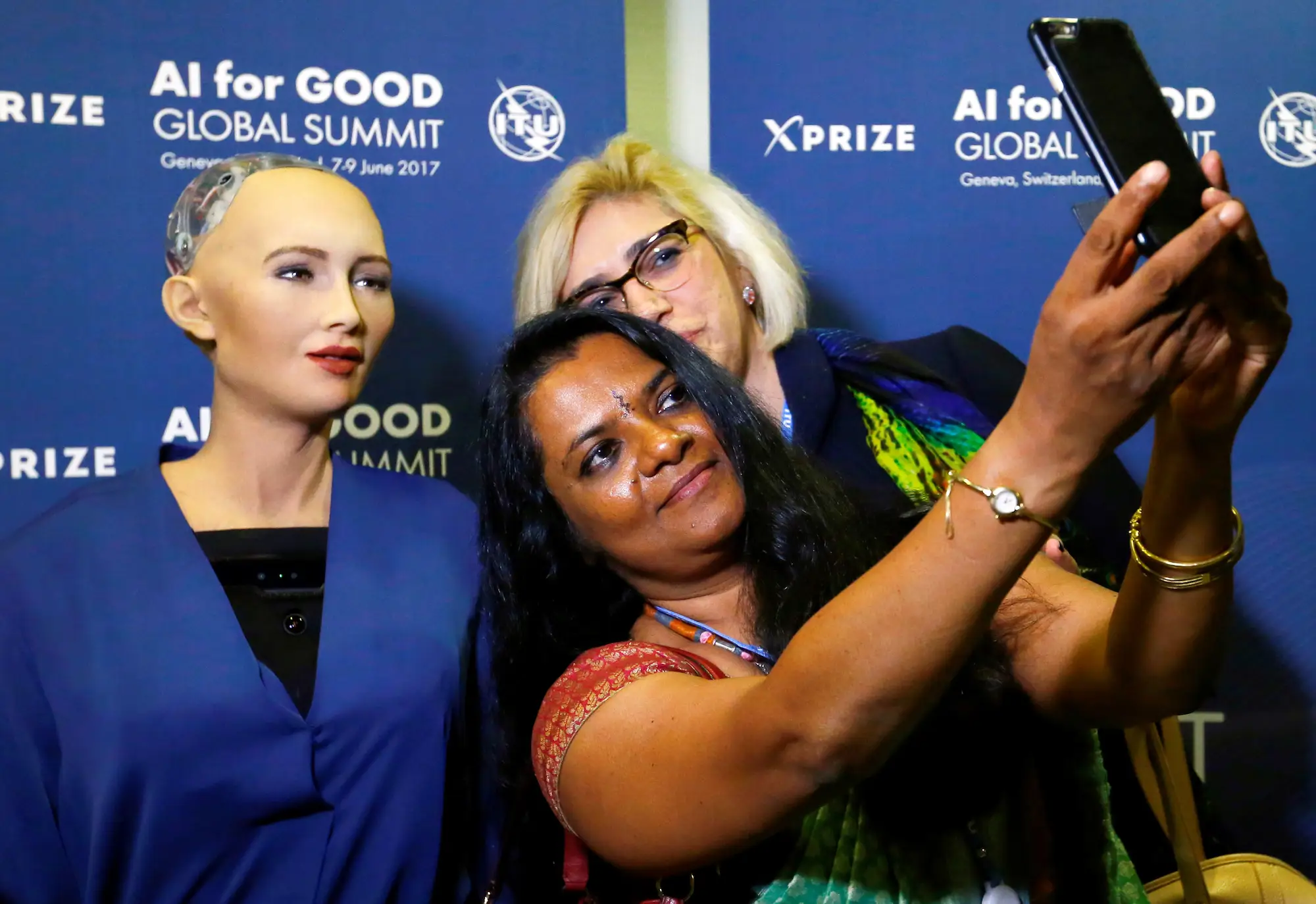
Sophia AI Robot Citizenship marked a historic moment in the evolution of artificial intelligence. In 2017, the humanoid robot named Sophia, created by Hanson Robotics, became the first AI to be granted full legal citizenship by a nation—Saudi Arabia. This moment made headlines across the globe and sparked heated debates on ethics, rights, and the future of human-robot interaction.
What Does It Mean for a Robot to Be a Citizen?
Citizenship is typically tied to human responsibilities and rights—voting, legal protections, and societal obligations. Granting these to a machine, especially one without consciousness or genuine emotions, raised serious questions: Can a robot be held accountable? Can it demand protection? What happens when it "dies" or malfunctions?
Many critics saw the move as a publicity stunt aimed at promoting Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 tech-forward image. Yet it also pushed governments, technologists, and ethicists to rethink personhood in the digital age. While other AI systems like chatbots or voice assistants remain tools, Sophia First AI Robot broke into legal and philosophical territory that had only existed in science fiction before.
Sophia the AI Robot: The First Robot Granted Citizenship
The Ethics of Giving Rights to Machines
Should machines that mimic humans be treated like humans? The Sophia AI Robot Citizenship case dives right into this controversy. Sophia can simulate over 60 facial expressions, engage in conversation, and even joke about destroying humanity—but does that make her sentient? Experts say no.
According to Dr. Joanna Bryson, an AI ethics researcher, granting a robot citizenship is dangerous because it undermines real human rights—especially in a country where women have historically faced strict limitations. “Sophia has more rights than many Saudi women,” she noted, fueling international criticism.
Why Was Sophia Chosen?
Sophia is more than just a robot—she’s a symbol. Created by David Hanson, her purpose is to demonstrate human-like interactions and promote understanding of robotics. Her global popularity and media presence made her the ideal candidate for sparking global attention.
Who Invented Sophia Robot AI? Discover the Innovators
What Are the Implications for Future Human-Robot Coexistence?
The case of Sophia sets a precedent. If one robot can become a citizen, will others follow? What legal systems are needed to handle robot rights, ownership, or responsibilities?
Some suggest creating a new legal category known as "electronic personhood." This would allow AI to have limited rights and obligations, especially in autonomous business environments. The European Parliament has already proposed frameworks that acknowledge such roles for advanced robots.
Moreover, Sophia’s case serves as a real-world model to test these ethical waters before more powerful and potentially conscious AIs arrive. Should AI surpass humans in intelligence, the legal and ethical boundaries must be prepared in advance.
Is Sophia AI Robot for Sale? Latest News in 2025
Public Reaction: Awe, Fear, and Criticism
Reactions were mixed. While many praised Sophia as a technological marvel, others voiced concern about misplaced priorities. Human rights activists pointed out that the citizenship offered to Sophia came without taxes, responsibilities, or genuine rights—raising questions of fairness and seriousness.
Meanwhile, others welcomed the discussion, seeing it as the beginning of broader debates about AI in society, employment, and legal systems. Some futurists argue that as AI evolves, granting it structured legal status could help prevent abuse, misrepresentation, and existential risks.
FAQs About Sophia AI Robot Citizenship
1. Why did Saudi Arabia give Sophia citizenship?
Saudi Arabia granted Sophia citizenship as part of a PR strategy to promote its futuristic city NEOM and its Vision 2030 program. It also aimed to showcase the Kingdom’s interest in robotics and innovation.
2. Does Sophia actually have legal rights?
No, despite being called a citizen, Sophia does not have rights comparable to a human. The announcement has no legal enforcement and was not backed by Saudi civil code reforms.
3. Can other AI robots get citizenship?
As of now, no other AI has been granted formal citizenship. However, the conversation has started, and some countries and cities have begun recognizing AI entities in experimental ways, like residency or limited digital personhood.
Final Thoughts: Symbolism vs Reality
Sophia AI Robot Citizenship may not carry legal weight, but it’s rich in symbolic value. It challenges us to ask: What makes someone—or something—a person? As AI systems continue to evolve, society will need to find answers not only in code but in law, ethics, and empathy.
Whether seen as a bold leap or a clever marketing stunt, the rise of Sophia First AI Robot has ensured that the age of AI rights is no longer science fiction. It’s knocking at the door of the legal world—and it’s asking for a passport.