Remember when entertainment robots meant clunky remote-controlled toys? That era is over. We're now experiencing a robotic renaissance where sophisticated AI companions blur the lines between technology and emotional connection. From empathetic companions easing loneliness to AI performers creating original art, these marvels have fundamentally transformed leisure and creativity. This definitive guide examines eight revolutionary categories shaping this dynamic field, exploring how sensory AI and emotional computing power the most advanced entertainment machines ever created. Discover how interactive robotic platforms are pioneering experiences you never thought possible.
Core Insight: Modern entertainment robots have evolved beyond toys into social companions and creative collaborators by leveraging emotional recognition AI, responsive behavior systems, and adaptive learning algorithms, making them uniquely positioned to address both entertainment and emotional needs.
The Evolution of Robotic Entertainment
The journey began with simple automatons in ancient civilizations, evolved through clockwork novelties of the Renaissance, and exploded with digital programmability in the 1980s. The true revolution began when machine learning algorithms fused with tactile sensors and emotional AI around 2010. Unlike industrial robots designed for repetitive tasks, entertainment robots demand nuanced interaction capabilities. Modern units incorporate voice pattern analysis, gaze tracking, and biometric response systems that adapt to individual users. This technological convergence has birthed entirely new categories of robotic entertainment that feel startlingly alive.
Exploring the Diverse Types of Entertainment Robots
1. Empathic Companion Robots
These sophisticated machines use multisensory AI to detect human emotions through vocal patterns and facial micro-expressions. Products like Paro the therapeutic seal robot respond to touch with nurturing behaviors, activating proven calming effects in dementia patients. What distinguishes this category is their adaptive personality algorithms that remember interaction history, creating genuine bonds while providing psychological benefits.
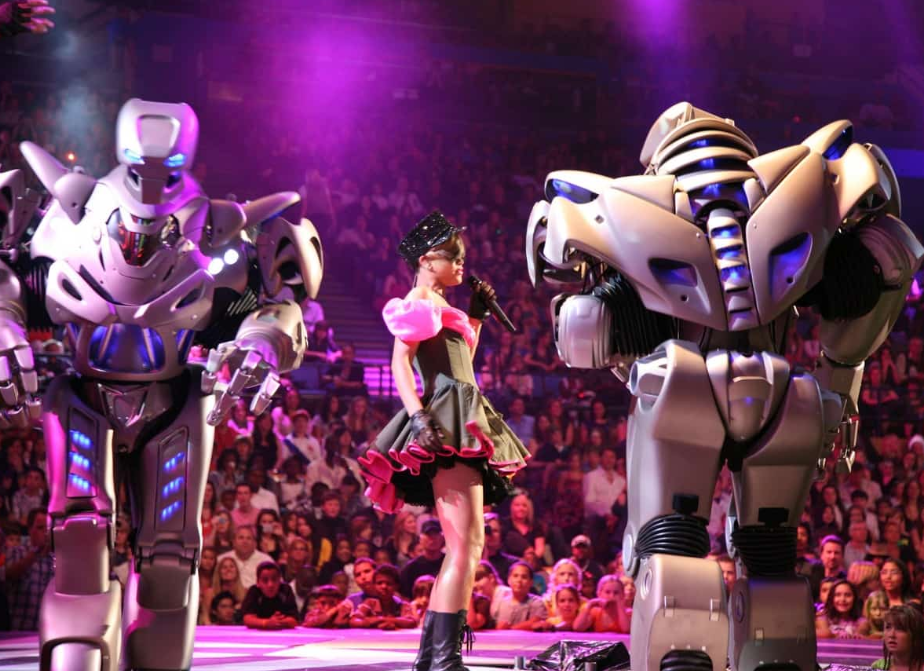
2. Interactive Performance Androids
Blending artistic expression with robotics, these creations can improvise musical compositions and analyze audience reactions in real-time. The humanoid robot Alter 3 employs chaotic neural networks to generate unpredictable movements, while Disney's stuntronics perform acrobatics impossible for humans. Their embedded physics engines calculate complex motion paths while maintaining expressive capabilities critical for artistic performance.
3. AI-Powered Creative Partner Systems
Artistic robots now generate poetry and conceptual art using generative adversarial networks (GANs). Sougwen Chung's installation D.O.U.G._ collaborates with humans through synchronized brushstrokes, learning from each interaction. This represents a paradigm shift beyond programmed art into collaborative creativity where robots develop unique artistic signatures through machine learning pattern analysis.
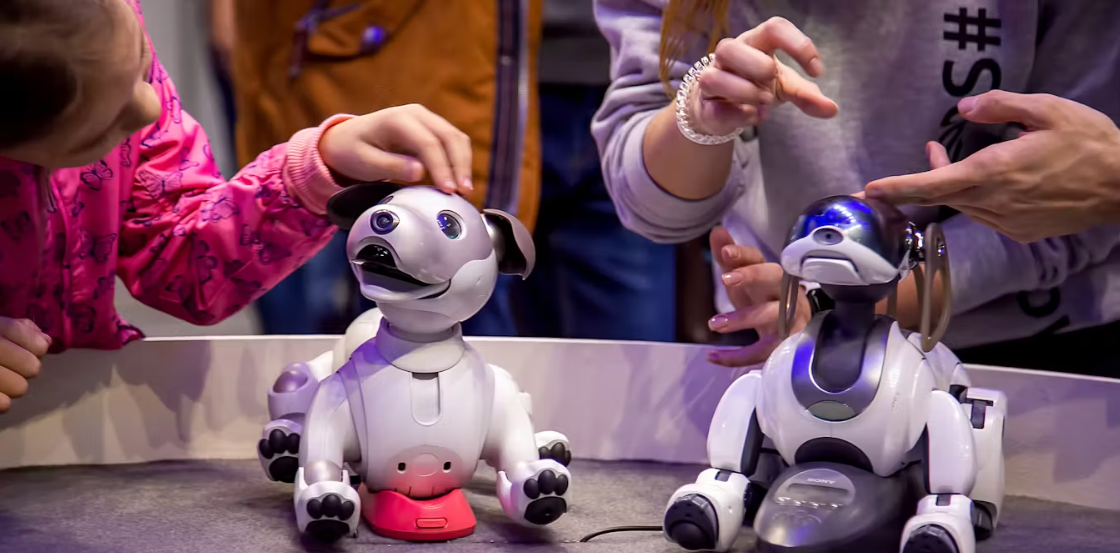
4. Responsive Pet Robots
Modern robotic pets like Sony's Aibo incorporate autonomous learning, developing individual personalities based on owner interactions. Their AI processes environmental stimuli using spatial awareness sensors and pattern recognition for authentic behavioral responses.
5. Competitive Gaming Drones
Autonomous drone racing represents a thrilling category where computer vision algorithms process real-time video feeds at 240fps for split-second navigation decisions. These machines calculate optimal racing lines while avoiding obstacles using simultaneous localization and mapping technology, demonstrating the cutting-edge application of real-time AI.
6. Sensory Immersion Platforms
Tactile feedback robots synchronize with media content through haptic suits and responsive furniture. Products like the Possessed Vest translate audio frequencies into physical sensations while immersive VR platforms like The VOID incorporate environmental effects that respond to user actions.
7. Neurologically Responsive Installations
The avant-garde of entertainment robots directly interfaces with brainwaves using EEG technology. Artist Lisa Park's Eunoia installation transforms brainwave patterns into water vibrations and soundscapes, creating personalized meditation environments that respond to mental states.
8. Cognitive Development Companions
Robots like Miko leverage child psychology frameworks and content recognition to deliver personalized educational entertainment. Their natural language processing understands developmental stages while emotional AI detects frustration to modify teaching approaches, representing the sophisticated potential of entertainment robotics beyond leisure.
Technical Framework Enabling Modern Entertainment Robotics
How Different Types of Entertainment Robots Utilize AI
The capabilities described depend on specialized technology stacks. Natural language processing algorithms analyze speech tone, sentiment, and context rather than just words. Computer vision systems interpret subtle facial cues with emotion classification models trained on millions of expressions. Reinforcement learning allows robots to refine behaviors based on reward feedback systems while knowledge graphs store memories of interactions.
Technical Deep Dive: The most advanced entertainment robots use multimodal sensor fusion combining visual, auditory, and tactile inputs to construct comprehensive environmental understanding. Predictive behavior engines then generate appropriate responses by combining deep learning models with personality matrices unique to each device.
Societal Impacts and Emerging Trends
These innovations raise profound questions about human-robot relationships. Japanese studies document seniors bonding with care robots while MIT experiments show children readily anthropomorphize educational bots. We're witnessing an entertainment evolution where:
Personalization algorithms create unique relationships with each user
Empathetic robots reduce dementia-related agitation by up to 60%
Creative bots challenge notions of artistic authenticity
The frontier involves bidirectional emotion transfer where humans begin interpreting robot emotional states, creating complex feedback loops predicted to transform entertainment psychology.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What distinguishes entertainment robots from industrial robots?
A: Unlike industrial robots focused on precision and repetition, entertainment robots prioritize emotional resonance, adaptability, and social interaction capabilities through specialized AI architectures.
Q: Can modern entertainment robots learn from their interactions?
A: Advanced models employ deep reinforcement learning where each interaction subtly adjusts behavioral parameters. Companion robots typically log thousands of interaction data points to refine personality matrices.
Q: How safe are these robots for children's development?
A: Studies show benefits in skill development but suggest balanced usage. Leading developmental psychologists recommend human-robot interaction supplementing rather than replacing human relationships during critical developmental windows.
Q: What emerging technology will most impact future entertainment robots?
A: Quantum computing promises exponential improvements in emotional prediction accuracy while neuromorphic chips will enable real-time sensory processing in compact form factors, leading to more lifelike interactions.
The Future Landscape
Entertainment robotics is converging with generative AI and biotechnology through artificial emotional intelligence development. The coming decade will bring hybrid entertainment forms including:
Musical robots improvising with human performers based on mood analysis
Robotic actors displaying complex emotional development throughout theatrical performances
Persistent companions with life-long learning profiles that grow with their owners
As affective computing advances, these devices won't just entertain us – they'll fundamentally redefine companionship and creative partnership in the digital age.