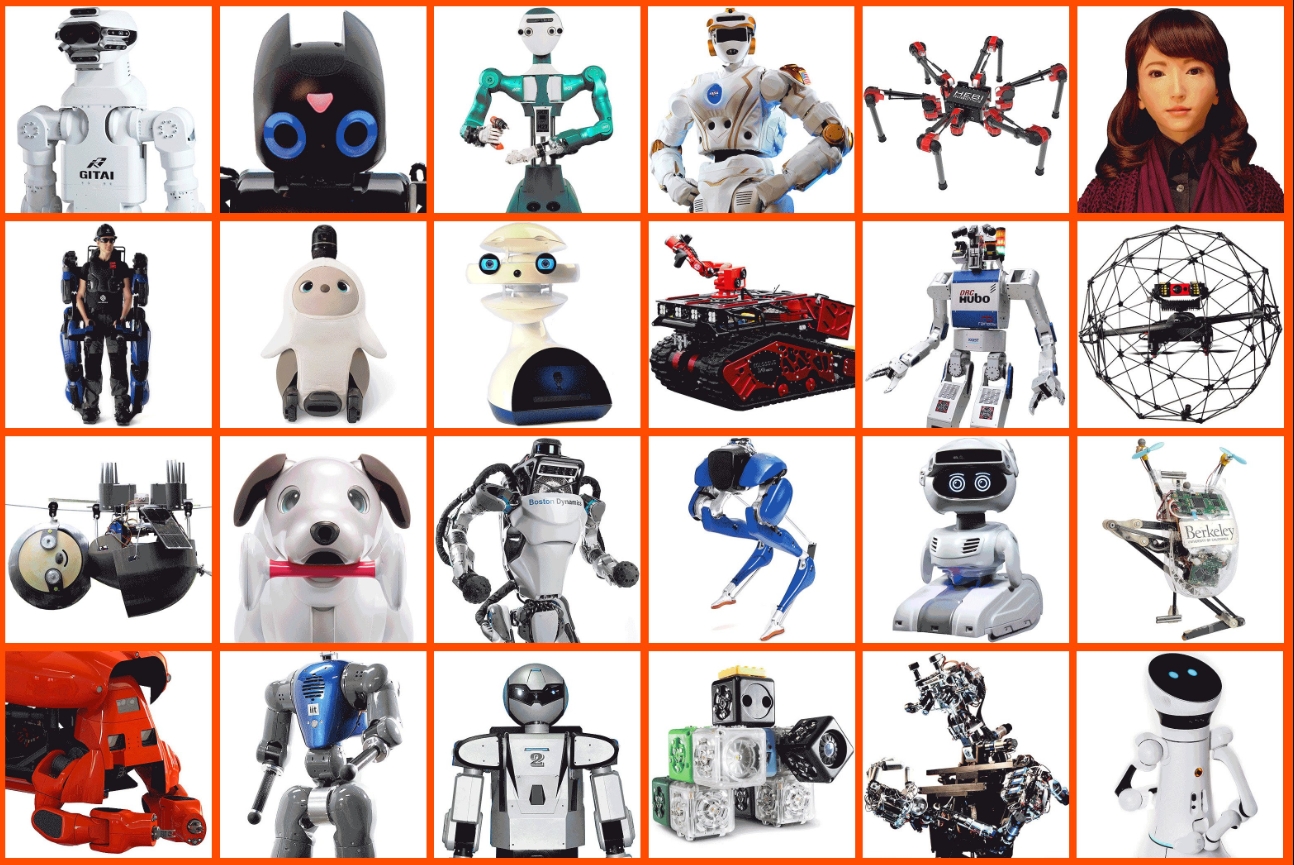
In the realm of technology, few concepts have captured the human imagination quite like robots. From the mythical automatons of ancient legends to the sophisticated machines of today, robots have evolved into a diverse family of robots, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes. This article delves into the fascinating world of robotics, exploring their historical development, the various types of robots that exist, and their real-world applications that are transforming industries and daily life. Join us as we uncover the evolution of robotics and discover how these mechanical marvels are shaping our future.
The Evolution of Robots
The concept of robots has deep roots in human history, spanning from ancient myths to modern technological marvels.
Early Concepts and Legends
In ancient Greek mythology, Hephaestus, the god of blacksmiths, created automated golden maidens to assist him in his workshop (Greek Mythology). Similarly, in Chinese legends, there are tales of mechanical beings created by inventors like Yan Shi. These early stories reflect humanity's fascination with creating artificial life forms.
Medieval and Renaissance Automata
During the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, inventors and artisans created mechanical devices known as automata. These included clockwork figures that could move and perform simple tasks. For example, Al-Jazari, a 12th-century Islamic scholar, designed humanoid automata that could serve drinks or play music. Leonardo da Vinci also sketched designs for a mechanical knight.
The Birth of Modern Robotics
The term "robot" was first coined in 1920 by Czech playwright Karel ?apek in his play R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots). However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that the first true robots were developed. In 1954, George Devol invented the Unimate, the first digitally operated programmable robot, which was later installed in a General Motors factory in 1961 (Britannica Robotics). This marked the beginning of industrial robotics.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Robotics
In recent decades, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have revolutionized robotics. Robots are now capable of learning from their environments, adapting to new situations, and performing complex tasks with greater autonomy. For instance, humanoid robots like ASIMO and Atlas have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in walking, object manipulation, and even interacting with humans.
Types of Robots
Within the family of robots, there are distinct categories that share common traits or roles. Here are some of the main types:
Industrial Robots
These are the workhorses of manufacturing, performing tasks such as welding, assembly, and material handling. Examples include the Unimate and modern collaborative robots (cobots) like YuMi and UR series. Industrial robots are crucial for efficiency and precision in large-scale production.
Humanoid Robots
Designed to resemble humans, these robots are often used in research and development. Famous examples include ASIMO, Atlas, and the Geminoid family, which are eerily lifelike (Robots Guide). Humanoid robots are particularly fascinating as they blur the line between machine and human.
Service Robots
These robots assist humans in various service-oriented tasks. They include domestic robots like the Roomba vacuum cleaner, as well as robots used in hospitality, retail, and healthcare. Service robots are becoming increasingly common in everyday life.
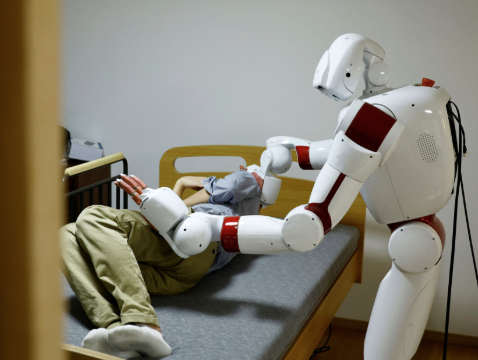
Medical Robots
From surgical robots like the da Vinci system to prosthetic limbs and rehabilitation devices, medical robots are transforming healthcare. They enable minimally invasive surgeries and help patients regain mobility, showcasing the life-saving potential of robotics.
Social Robots
These robots are designed to interact with humans on a social level, providing companionship or assistance. Examples include Pepper, Jibo, and Paro, a therapeutic robot seal. Social robots are particularly valuable in elder care and autism therapy.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars and trucks represent a significant leap in robotics, promising to revolutionize transportation. Companies like Waymo and Tesla are at the forefront of this technology, with autonomous vehicles already being tested in real-world scenarios.
Drones
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have become ubiquitous, used for everything from aerial photography to delivery services and military operations. Drones are a prime example of how robotics can extend human capabilities into the air.
Comparison of Robot Types
To better understand the diversity within the family of robots, let's compare some key types based on their features and primary use cases:
| Type | Key Features | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Robots | Precision, strength, repeatability | Manufacturing, assembly, welding |
| Humanoid Robots | Human-like appearance, dexterity | Research, human-robot interaction |
| Service Robots | Task-specific automation | Cleaning, delivery, hospitality |
| Medical Robots | Precision, minimally invasive | Surgery, rehabilitation, therapy |
| Social Robots | Interaction, emotional response | Companionship, education, therapy |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Self-driving capability | Transportation, logistics |
| Drones | Aerial mobility, imaging | Photography, surveillance, delivery |
Real-World Applications of Robots
Different members of the family of robots find applications across various sectors, enhancing efficiency, safety, and innovation.
Manufacturing and Industry
Industrial robots have been a staple in manufacturing since the 1960s. They handle repetitive and dangerous tasks, improving productivity and reducing human error. Today, over 3 million industrial robots are in operation worldwide, with the automotive and electronics industries being the largest users.
Healthcare and Medicine
In healthcare, robots assist in surgeries, rehabilitation, and patient care. Surgical robots like the da Vinci system allow for precise, minimally invasive procedures. Exoskeletons help patients with mobility issues, and social robots provide companionship for the elderly.
Exploration and Space
Robots are crucial for exploring environments that are too dangerous or inaccessible for humans. Mars rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance have provided invaluable data about the Red Planet. In space, robots like the Canadarm2 on the International Space Station perform maintenance and assembly tasks.
Domestic and Consumer Use
Consumer robots like the Roomba have made household chores easier, while smart home devices incorporate robotic elements for security and convenience (Proven Robotics). Delivery robots are also emerging, bringing goods directly to consumers' doorsteps.
Entertainment and Education
Robots are used in theme parks, museums, and educational settings to entertain and educate. For example, RoboThespian performs comedy routines, while educational robots like Dash and Dot teach children coding and problem-solving skills.
Military and Security
Military robots are used for reconnaissance, bomb disposal, and logistics. Security robots patrol facilities, monitoring for intruders and anomalies.
The Future of Robotics
As technology advances, robots are poised to become even more integrated into our daily lives.
Emerging Technologies
Developments in AI, machine learning, and materials science are leading to more capable and versatile robots. Evolutionary robotics, where robots are designed using evolutionary algorithms, is pushing the boundaries of what robots can achieve (Evolutionary Robotics).
Ethical Considerations
With increased robot autonomy comes ethical questions about responsibility, privacy, and the impact on employment. For instance, social robots raise concerns about emotional bonding and privacy, while industrial robots may displace human workers (Ethics in Robotics). It's crucial to address these issues as robots become more prevalent.
Integration into Society
Robots are expected to play a significant role in future societies, from assisting in elder care to performing tasks in hazardous environments. Their integration will require careful planning and regulation to ensure they benefit humanity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a family of robots?
A family of robots refers to groups of robots that share common characteristics, purposes, or are developed from a common lineage. For example, industrial robots, humanoid robots, and service robots can be considered different families within the broader category of robots.How have robots evolved over time?
Robots have evolved from simple mechanical devices to complex, AI-driven machines. Early robots were primarily industrial, performing repetitive tasks. Today, robots are diverse, with capabilities ranging from autonomous driving to social interaction, thanks to advancements in AI and robotics technology.What are some real-world applications of robots?
Robots are used in manufacturing for assembly and quality control, in healthcare for surgery and rehabilitation, in exploration for space and underwater missions, in domestic settings for cleaning and companionship, and in entertainment for education and amusement.Are there robots that can think and feel like humans?
While robots can simulate human behavior and interact socially, they do not possess consciousness or emotions. However, advancements in AI are making robots more capable of understanding and responding to human emotions.How do robots learn and adapt to new situations?
Robots learn through various methods, including machine learning, where they process data to improve performance, and reinforcement learning, where they learn from trial and error. Some robots also use evolutionary algorithms to adapt their behavior over time.
Conclusion
The family of robots is vast and varied, each type bringing unique capabilities and applications to the table. From the early myths to the sophisticated machines of today, robots have come a long way and continue to evolve. As we look to the future, the integration of robots into society will require not only technological advancements but also thoughtful consideration of ethical implications. By understanding the different types of robots and their real-world applications, we can better appreciate the impact they have on our world and prepare for the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.