Explore how AI Car systems navigate without human input, the key pros and cons of Self-Driving Car systems, and the regulatory landscape shaping their rollout. Delve into sensor fusion, deep learning algorithms, ethical dilemmas, and consumer adoption trends, offering a balanced view of benefits like reduced accidents versus challenges such as cybersecurity risks.
Introduction to AI Car Revolution
The rise of the AI Car marks a pivotal shift in automotive history. By combining advanced sensors and powerful onboard computing, these vehicles promise safer roads and more efficient transportation. As cities grow and commutes lengthen, the pressure on traditional driving models has never been greater.
In 2025, the global autonomous vehicle market is projected at USD 273.75 billion, growing at a 36.3 % CAGR through 2034. By 2025, autonomous vehicles’ revenue is expected to more than double from USD 208 billion in 2023 to USD 428.3 billion. These numbers underscore the rapid momentum behind AI Car innovation and widespread adoption.
Expert Insight
“Sensor fusion and deep learning are the backbone of reliable self-driving systems,” says Dr. Maria Chen, lead AI engineer at a major autonomous startup. “The fusion of radar, LiDAR, and camera data allows an AI car to 'see' in 360°, improving detection accuracy by over 40 % compared to single-sensor models.”
Core Technologies Behind Self-Driving Technology
Sensor Fusion and Perception
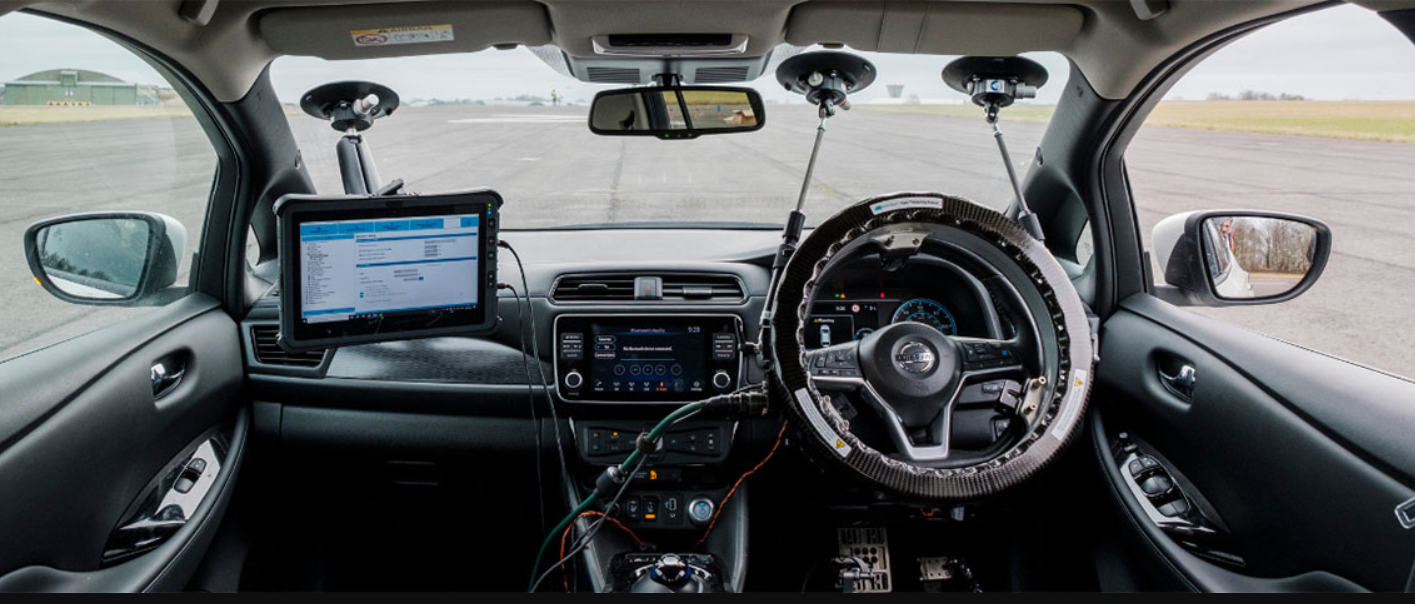
AI Car systems rely on an array of sensors: LiDAR, radar, ultrasonic, and high-resolution cameras. Sensor fusion algorithms merge these streams into a coherent environmental model. This allows autonomous vehicles to detect pedestrians, cyclists, and other obstacles in real time.
Deep Learning and Decision-Making
Deep neural networks power the decision-making process inside an AI Car. Convolutional networks identify objects, while reinforcement learning models optimize driving policies. Continuous updates from cloud-based training ensure the AI Car adapts to new road scenarios and edge cases.
Connectivity and Mapping
Real-time mapping and V2X communications enhance vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure interactions. Autonomous vehicles share traffic updates, road hazards, and optimal routing information, creating a cooperative driving ecosystem.
Weighing Self-Driving Car Pros and Cons
Self-Driving Car Benefits
The main Self-Driving Car benefits include:
Reduced accidents: Over 90 % of crashes are caused by human error. Autonomous systems aim to lower this drastically.
Increased mobility: Elderly and disabled passengers gain independence with door-to-door automated transit.
Optimized traffic flow: AI cars can platoon and adapt speeds, cutting congestion by up to 30 %.
Self-Driving Car Challenges
Despite the promise, several hurdles remain:
Cybersecurity risks: Connected vehicles can be targeted by hackers.
Ethical dilemmas: Decision-making in unavoidable crash scenarios raises moral questions.
Regulatory uncertainty: Laws differ across regions, slowing nationwide deployment.
Case Study
In Phoenix, a pilot fleet of 100 autonomous taxis completed over 10,000 rides in six months, reporting a 25 % reduction in average wait times and zero at-fault accidents. Riders cited comfort in using Self-Driving Technology for daily commutes and express trips.
Regulatory Landscape Shaping Autonomous Vehicles
Governments worldwide are crafting rules for Autonomous Vehicles. The U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) issues guidelines on safe testing, while the EU focuses on data privacy and liability frameworks. Harmonizing these regulations is crucial for cross-border mobility.
Public trust grows as standards mature. Insurance models evolve to cover Self-Driving Car usage, with specialized AI Car Insurance products emerging to address liability shifts from driver to manufacturer.
Consumer Adoption of AI Cars
Surveys indicate 65 % of adults would ride in a Self-Driving Car within five years. Early adopters cite convenience and safety, while skeptics worry about technology reliability. Automakers partner with ride-hailing services to introduce autonomous ride-shares, easing public exposure.
FAQs
1. What is an AI Car?
An AI Car combines robotics, machine learning, and sensor fusion to navigate and drive without human input.
2. How safe are Self-Driving Cars?
While autonomous vehicles show a strong safety record in trials, real-world deployment still faces edge-case challenges and regulatory oversight.
3. When will Autonomous Vehicles be widespread?
Experts predict significant adoption by 2030, with pilot programs in major cities by 2026.
4. What are the costs of Self-Driving Technology?
Current costs for Level 4 sensor suites exceed USD 20,000 per vehicle, but prices are falling with mass production.
Conclusion
The future of mobility is unmistakably tied to the evolution of the AI Car. As Self-Driving Technology matures, we can expect safer roads, greater accessibility, and smarter urban planning. Balancing innovation with ethical and regulatory considerations will ensure that autonomous vehicles revolutionize tomorrow’s roads for the benefit of all.